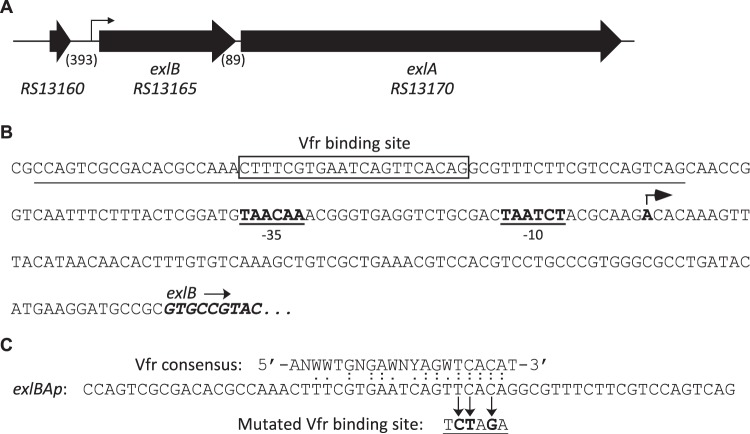
FIG 1.
Features of the exlBA chromosomal region. (A) The exlBA genes as well as the upstream gene are depicted by thick arrows with the nomenclature from Pseudomonas Genome Database website (28; www.pseudomonas.com). The lengths of intergenic sequences (in base pairs) are in parentheses. The exlBA promoter (exlBAp) region identified in this study is represented by a thin arrow. (B) Sequence of the exlBA promoter. The three first codons of exlB are in italics and boldface. The nucleotide identified as potential exlBA TSS found by circularization assay is in boldface and pinpointed by an arrow, with the corresponding putative −10 and −35 boxes indicated. The Vfr binding site (VBS) is boxed. Underlined is the 60-mer sequence used in EMSA and provided in panel C. (C) Comparison of the Vfr consensus sequence to the sequence found in exlBAp. The mutated VBS used in EMSA and created in the chromosome of the VBM mutant is also indicated.