FIG 5.
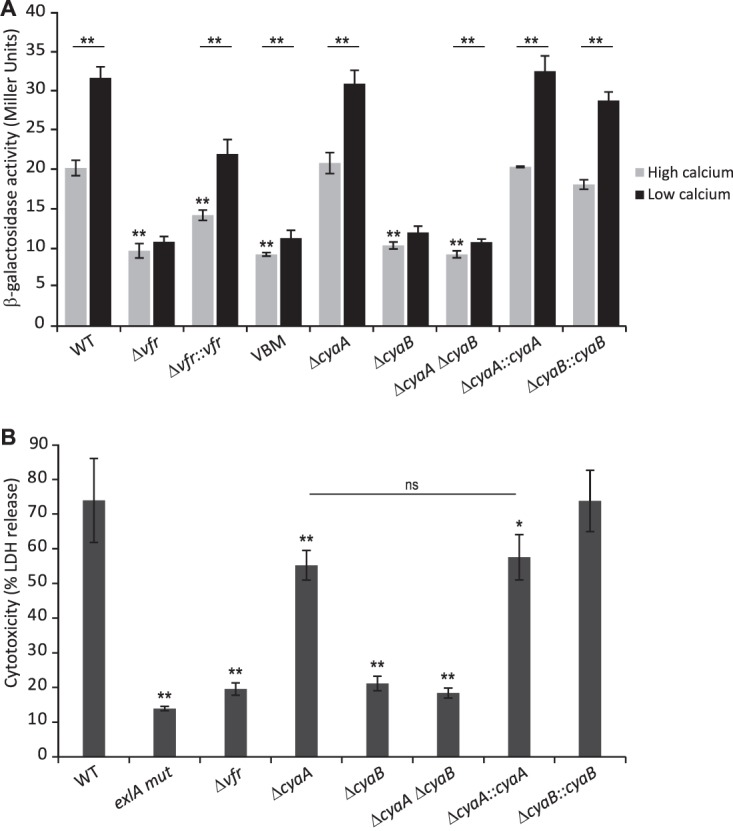
Vfr controls exlBA expression in a cAMP-dependent manner. (A) β-Galactosidase activities of the indicated wild-type (WT), mutant, and complemented strains carrying a chromosomal exlA-lacZ transcriptional fusion. Strains were grown in LB medium supplemented with CaCl2 (high-calcium condition) or EGTA-MgCl2 (low-calcium condition) at 37°C to an OD600 of 1.5. (B) ExlA-dependent cytotoxicity on A549 epithelial cells of the indicated wild-type (WT), vfr, cyaA, and/or cyaB mutant, and corresponding complemented strains measured after 4.5 h of infection (MOI of 10). The experiments were performed in triplicate, and the error bars indicate the standard deviations. The P value was determined using Mann-Whitney U test and is indicated above the error bars by * (P < 0.05) or ** (P < 0.01) when the difference from the wild-type strain is statistically supported. In panel A, the asterisks above the horizontal line compare each strain under the two different growth conditions. Please note that in panel B, while the ΔcyaA mutant seems slightly less cytotoxic than the wild-type strain, its phenotype is not complemented (ns, not supported by statistics) and is probably due to genetic manipulation.
