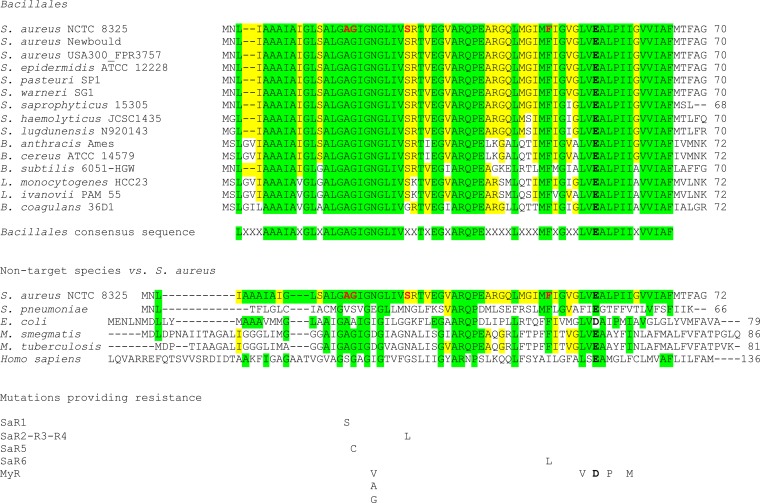
FIG 2.
Amino acid sequence alignments of the ATP synthase subunit C for selected species. First, the alignments for several species of Bacillales present a consensus sequence, highlighted in green. Amino acids additionally identical to those of S. aureus are highlighted in yellow. Amino acids mutated in TO/FC04-100-resistant mutants are in red and bold characters in the S. aureus NCTC 8325 sequence. Also shown below the Bacillales consensus sequence are the alignments for some bacterial species not targeted by TO. The changes in amino acids found in TO/FC04-100-resistant S. aureus (SaR1 to SaR6) are indicated below the alignments. The essential ion-binding glutamate (aspartate in E. coli) is indicated in bold black. Changes in amino acids reported for the bedaquiline-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Mycobacterium smegmatis (MyR denotes a mixture of these two species) are also indicated below the alignments (40).