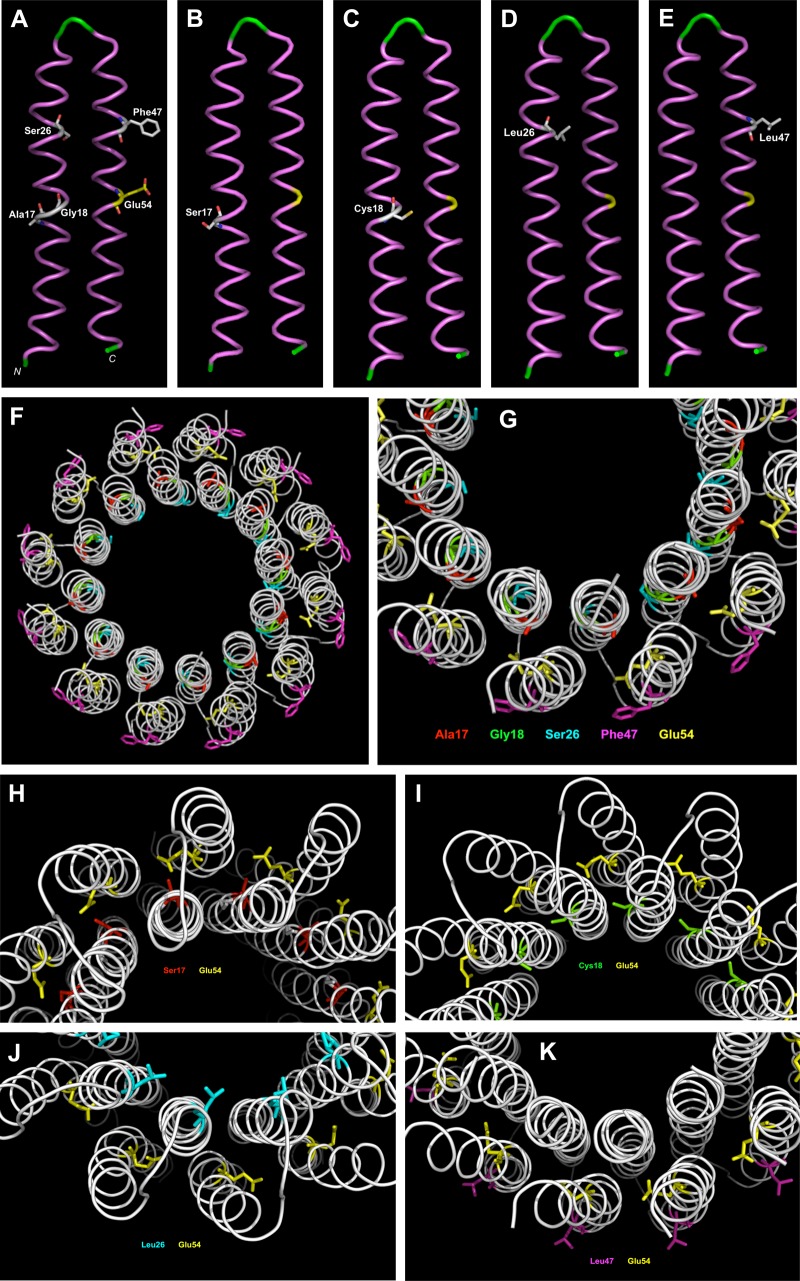
FIG 3.
Monomeric and multimeric models of ATP synthase subunit C built, respectively, on homology with templates of PDB accession numbers 1WU0 and 3ZO6, using the SWISS-MODEL server. (A) Position of amino acids (in white) implicated in high-level TO resistance in the wild-type polypeptide. Essential amino acid Glu54 is in yellow. (B) Position of Ser17 mutation in SaR1. (C) Position of Cys18 mutation in SaR5. (D) Position of Leu26 mutation in SaR2, SaR3, and SaR4. (E) Position of Leu47 mutation in SaR6. (F) Overview of the multimeric assembly of ATP synthase subunit C. (G) Position of amino acids (Ala17, red; Gly18, green; Ser26, cyan; Phe47, magenta) implicated in resistance in the wild-type multimeric assembly. Glu54 is also shown in yellow. (H) Position of the Ser17 mutation in the multimeric assembly in SaR1. (I) Position of the Cys18 mutation in the multimeric assembly in SaR5. (J) Position of the Leu26 mutation in the multimeric assembly in SaR2, SaR3, and SaR4. (K) Position of the Leu47 mutation in the multimeric assembly in SaR6. The models were drawn using PyMOL software (version 1.8.7.0; DeLano Scientific, San Francisco, CA).