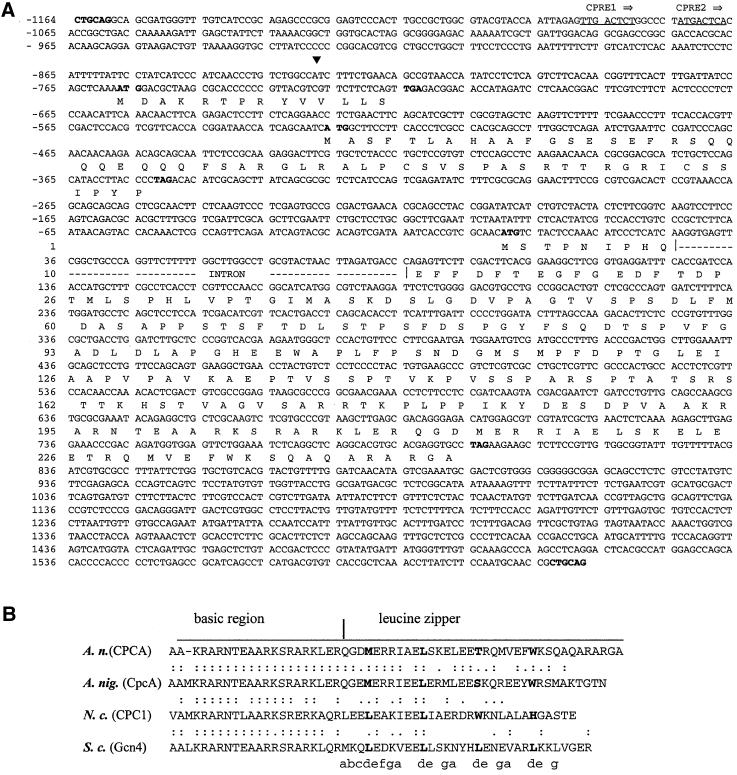
Figure 1.
DNA and deduced amino acid sequences of A. nidulans cpcA. (A) Nucleotide sequence of the PstI DNA fragment containing the entire cpcA gene. The transcriptional start site is indicated by a solid triangle. The CPREs are underlined. PstI restriction sites as well as the start and stop codons of uORF1, uORF2, and the cpcA open reading frame are in bold. The cpcA intron interrupting the open reading frame is indicated by a broken line. The numbers of nucleotide and amino acid sequences are shown on the left relative to the AUG start codon of cpcA. (B) Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences of the bZIP motif from CPCA amino acid positions 189–245 at the C terminus of the deduced protein (A. nidulans), CpcA (A. niger), CPC1 (N. crassa), and Gcn4p (S. cerevisiae). The basic DNA-binding domain and the leucine-zipper region are indicated by a horizontal bar. Amino acid residues at heptad positions (d) in the leucine-zipper region are shown in bold. Amino acid residues at the e and g positions are supposed to participate in dimer stabilization and electrostatic interactions (Durr et al., 1999).