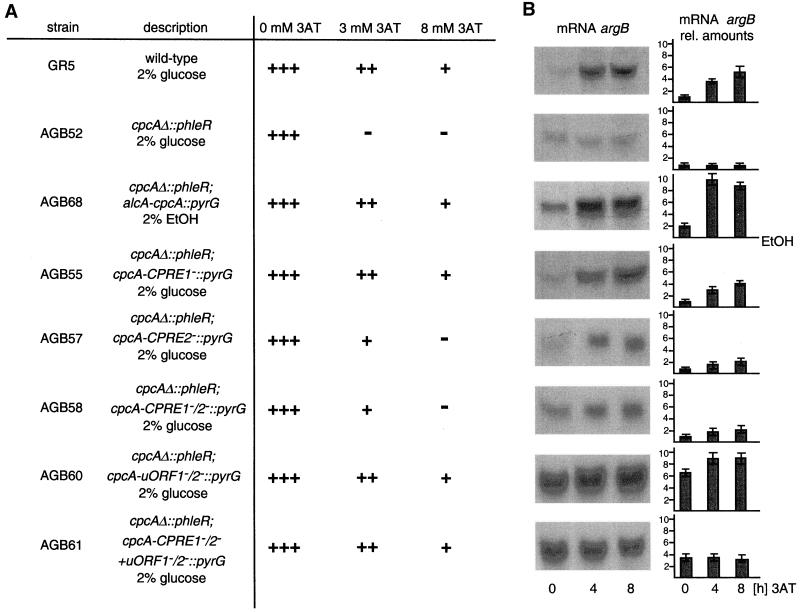
Figure 3.
Influence of various cpcA alleles on growth and mRNA amounts of the cross-pathway regulated argB gene. (A) Conidia of A. nidulans wild-type strain A234 and the cpcA mutant AGB51 (cpcAΔ) were dropped on minimal medium containing 0, 3, or 8 mM 3AT, respectively, to induce amino acid starvation. Colony growth was scored after incubation for 5 d at 30°C and is indicated as +++ for normal growth, ++ for reduced, + for barely growing colonies, and − for no growth. In strain AGB68 (cpcAΔ; alcA-cpcA), the open reading frame of A. nidulans cpcA is expressed under the control of the alcA promoter in the cpcA mutant background. Growth of the wild-type and the cpcAΔ mutant strain were unaffected by ethanol as carbon source. Strains AGB55 (cpcAΔ; cpcA-CPRE1−), AGB57 (cpcAΔ; cpcA-CPRE2−), AGB58 (cpcAΔ; cpcA-CPRE1−/2−), AGB60 (cpcAΔ; cpcA-uORF1−/2−), and AGB61 (cpcAΔ; cpcA-CPRE1−/2− + uORF1−/2−) were analyzed similarly. (B) RNAs were isolated from the strains described in A after growth under amino acid starvation conditions for 0, 4, and 8 h, respectively. mRNA amounts were equalized in parallel with the use of the constitutively expressed gpdA gene as probe. argB mRNAs are shown as autoradiography and as fold differences setting 0 3AT level of the wild type as 1.0.