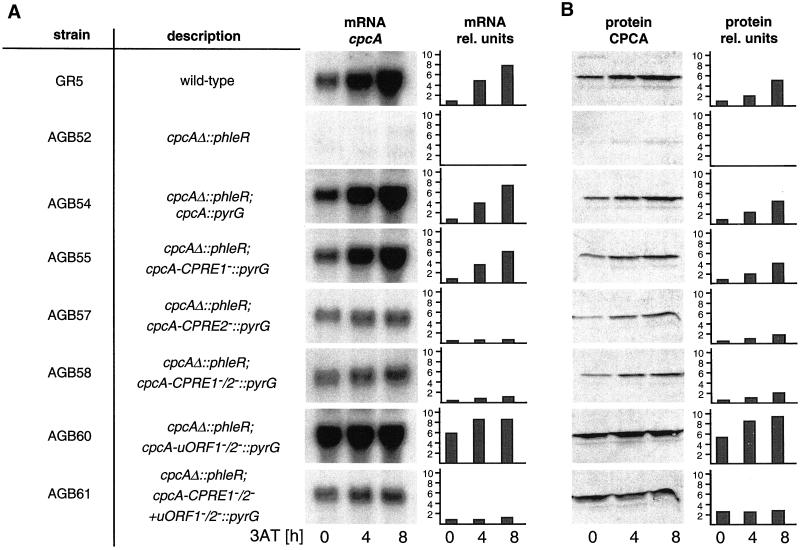
Figure 5.
Regulation of cpcA expression in A. nidulans. (A) Analysis of cpcA mRNA levels. Wild-type strain A234 and the cpcA mutant strains AGB51, AGB54, AGB55, AGB57, AGB58, AGB60, and AGB61 (Table 1) were grown overnight at 30°C in liquid minimal medium with glucose. At time 0, the amino acid analog 3AT was added to 10 mM to induce histidine starvation. Mycelia were harvested at the indicated times. The amount of RNA per lane was equalized by phosphorimaging with the use of the constitutively expressed gpdA gene as control probe and was then probed with the use of radioactively labeled cpcA cDNA. (B) Western analysis of CPCA. Crude protein extracts of the strains described in A were isolated after growth under nonstarvation (0) and 4 and 8 h under amino acid starvation conditions. CPCA amounts were determined by cross-reaction of 20 μg of crude protein extract of each strain with the Gcn4-specific rabbit antibodies. Quantification of CPCA protein was performed by comparison with a standardized Western hybridization with the use of different amounts of purified yeast Gcn4. In addition, a nonspecific band of lower molecular weight was used as internal standard. All Northern hybridizations and Western blots were performed in parallel on the same membranes to allow a comparison between cpcA alleles. cpcA mRNA and CPCA protein amounts are shown as autoradiography and as relative units. The amounts for wild type under nonstarvation conditions were set as 1.