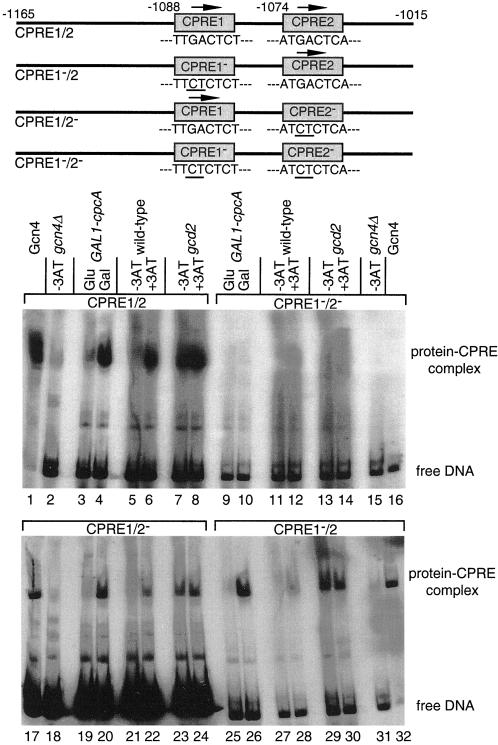
Figure 6.
In vitro DNA binding activity of Gcn4p and CPCA derived from various yeast extracts. DNA fragments used and the positions of integrated point mutations are shown schematically. A 151-bp DNA fragment from the cpcA promoter was used that contained both putative CPCA recognition elements (CPRE1/2, lanes 1–8). Additionally, point mutations were integrated in CPRE1 (CPRE1−/2, lanes 25–32), CPRE2 (CPRE1/2−, lanes 17–24), or both (CPRE1−/2−, lanes 9–16). All DNA fragments were radioactively labeled and incubated with 10 μg of protein extracts. Crude protein extracts of yeast wild-type H1515 and the gcd2 mutant strain RH1378 were isolated after 8 h of growth under nonstarvation (−3AT) and amino acid starvation conditions (+3AT). CPCA of A. nidulans was expressed under control of the yeast GAL1 promoter in the yeast gcn4Δ mutant strain RH1408. Protein extracts were isolated after 8 h on minimal medium containing glucose (Glu) or galactose (Gal) as sole carbon source, respectively. Purified Gcn4 protein expressed in E. coli was used as positive control; protein extracts of the gcn4Δ mutant strain RH1408 were used as negative control. Protein–DNA complexes were separated from unbound DNA by PAGE and visualized by autoradiography.