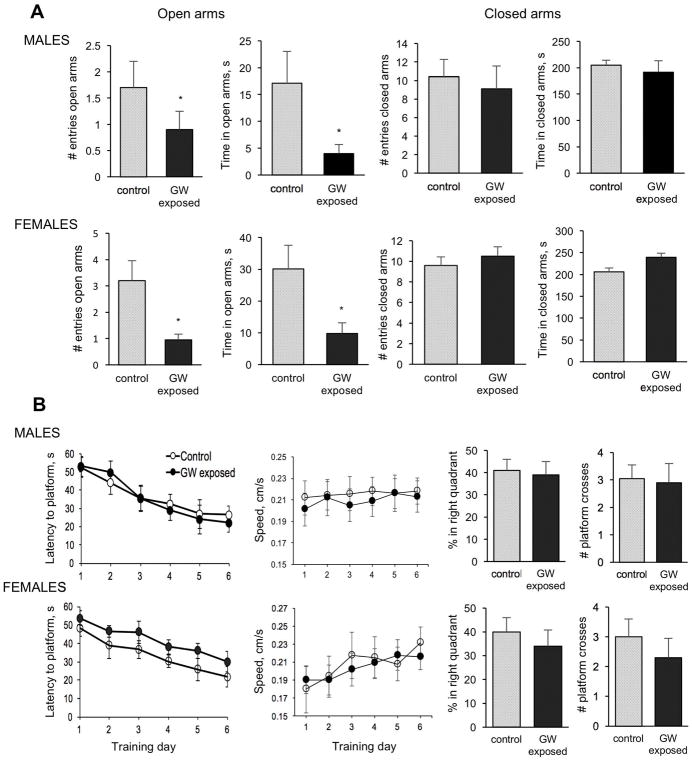
Figure 1.
Effect of exposure to GW-related chemicals and stress on anxiety, learning and memory. A. Anxiety. Exposure causes increased anxiety revealed in the Plus Maze test as both GW-exposed female and male mice did not enter as often and did not spent as much time as control mice in open arms. Two-way ANOVA for the number of entries into the open arms found a main effect of exposure (F= 4.31; p<0.05) with no effect of sex and no interactions. For time spent in open arms there was a main effect of exposure (F=4.9; p = 0.03) and no effect of sex and no interaction between factors. B. Learning and memory in the water maze. No significant differences in the escape latency and comparable swim speed between exposed and control female and male mice were observed during the 6 days of training trials. The probe trial performed twenty-four hours after the last training trial to test mice’s memory also showed no significant differences between groups for any of the analyzed parameters.