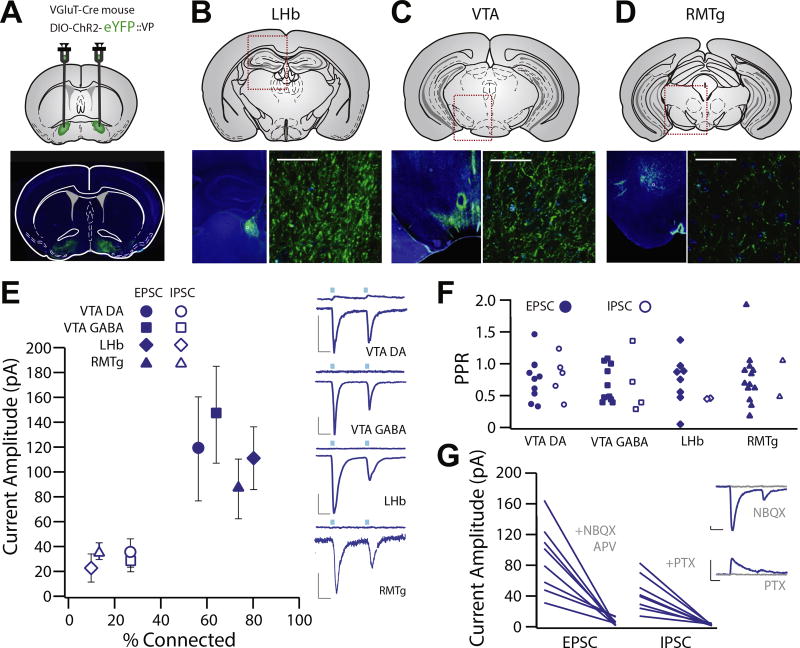
Figure 4.
Glutamatergic ventral pallidum (VP) neurons exhibit functional projections to the lateral habenula (LHb), ventral tegmental area (VTA), and rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg). (A–D) Experimental schematic and widefield images showing floxed channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) with enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (eYFP) injection sites to the VP of VGluT2-Cre mice and terminal fields in the LHb (B), VTA (C), and RMTg (D). (E) Patch clamp recordings were made of neurons in the terminal fields of vesicular glutamate transporter–positive VP neurons in the LHb (n = 20, capacitance = 17.63 ± 1.32 pF), RMTg (n = 15, capacitance = 26.83 ± 2.56 pF), and VTA (dopamine [DA] neuron n = 14, capacitance = 55.53 ± 5.097 pF, gamma-aminobutyric acid [GABA] neuron n = 14, capacitance = 19.96 ± 1.64). Recordings made at −70 mV revealed robust inward excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) (LHb: 80.0% connected, −89.7 ± 20.5 pA; RMTg: 73.3% connected, −98.6 ± 23.4 pA; VTA DA: 64.3% connected, −113.4 ± 43.4 pA; VTA GABA: 57.1% connected, −104.9 ± 40.6 pA), and recordings made at 0 mV revealed infrequent outward inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) (LHb: 10% connected, 33.5 ± 19.6 pA; RMTg: 13.3% connected, 32.5 ± 5.5 pA; VTA DA: 42.8% connected, 31.8 ± 7.2 pA; VTA GABA: 35.7% connected, 83.2 ± 44.6 pA). There was no difference between areas with respect to proportion of neurons exhibiting light-evoked currents, and EPSCs were observed more frequently than IPSCs [t test between proportions; VTA DA χ2(1) = 1.25, p = .26; VTA GABA χ2(1) = 1.25, p = .26; LHb χ2(1) = 14.04, p < .001; RMTg χ2(1) = 10.63, p = .001]. (F) There was no significant difference in EPSC or IPSC paired-pulse ratio (PPR) in any region (VTA DA: t4 = 0.6941, p = .5258; VTA GABA: t3 = 0.2195, p = .8403; LHb: t2 = 0.0187, p = .9867; RMTg: t1 = 0.7603, p = .5862) or in PPR between any brain region in terms of EPSC (one-way analysis of variance, EPSC F3 = 0.2552, p = .8572; mean VTA DA = 0.637 ± 0.091, VTA GABA = 0.784 ± 0.139, LHb = 0.691 ± 0.122, RMTg = 0.654 ± 0.116) or IPSC amplitude (one-way analysis of variance, IPSC F3 = 0.2487, p = .8605; VTA DA = 0.794 ± 0.166, VTA GABA = 0.849 ± 0.193, LHb = 0.620 ± 0.190, RMTg = 0.709 ± 0.265). (G) We verified that outward EPSCs were blocked by the combination of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists (6-nitro-7-sulfamobenzoquinoxaline-2-3-dione [NBQX] and D, L-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid [APV] at 100 µM), and outward IPSCs were blocked by the chloride channel blocker picrotoxin (PTX; 50 µM). Scale bars: 20 pA, 20 ms.