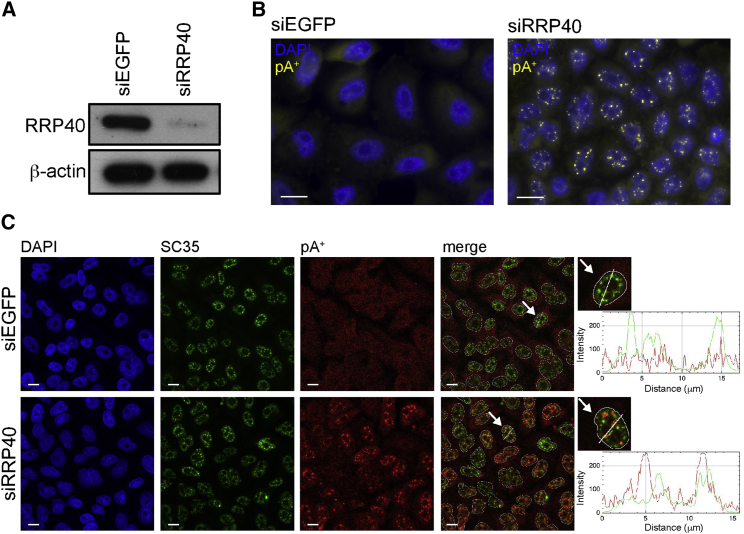
Figure 1.
RNA Exosome Depletion Leads to the Formation of Distinct Nuclear pA+ RNA Foci
(A) Western blotting analysis of RRP40 levels in HeLa cells treated with control siRNA (siEGFP) or siRNA targeting RRP40 (siRRP40). β-actin was used as a loading control.
(B) RNA-FISH analysis of pA+ RNA in control (siEGFP) or RRP40-depleted (siRRP40) HeLa cells. pA+ RNA, detected with an oligo(dT)-LNA probe (Thomsen et al., 2005), is shown in yellow, and nuclear DAPI stain is shown in blue.
(C) Co-localization analysis of pA+ RNA foci with the speckle marker SC35 using cells from (B). Confocal images of SC35 immunofluorescence (IF) signal in green, pA+ RNA-FISH signal in red, and DAPI stain in blue. SC35 IF and RNA-FISH signals were merged (merge). Arrows point to cells that were used for line scan analyses, and zoom-ins of the relevant cells are shown at the right of the corresponding panel. Line scan profiles represent IF and RNA-FISH signal intensities along the drawn line. Dashed lines represent outlines of nuclei. pA+ RNA was detected as in (B).
Scale bars, 10 μm.