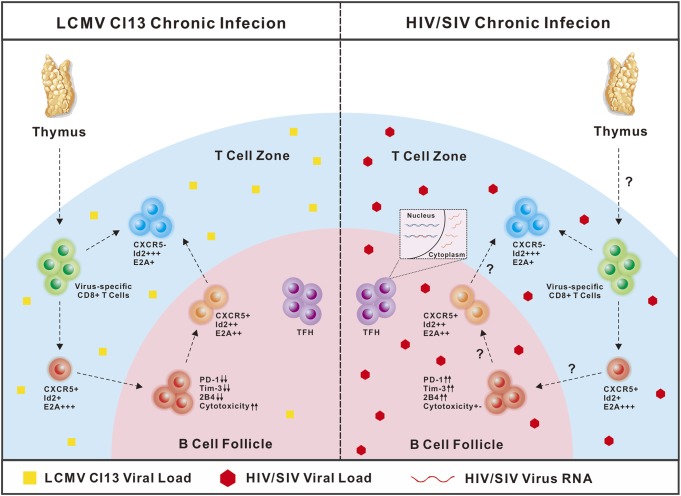
Figure 1.
Comparison of CXCR5+CD8 T cells in lymphocytic choromeningitis virus (LCMV)-Cl13 and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. In chronic LCMV-Cl13 infection, viruses seldom infect B-cell follicles, thus B-cell follicles function as a sanctuary for CXCR5+CD8 T cells to prevent rapid exhaustion. In contrast, HIV virus preferentially targets TFH cells in B-cell follicles for productive and latent infection, thus accumulating high antigen loads in B-cell follicles may drive more severe exhaustion of CXCR5+CD8 T cells.