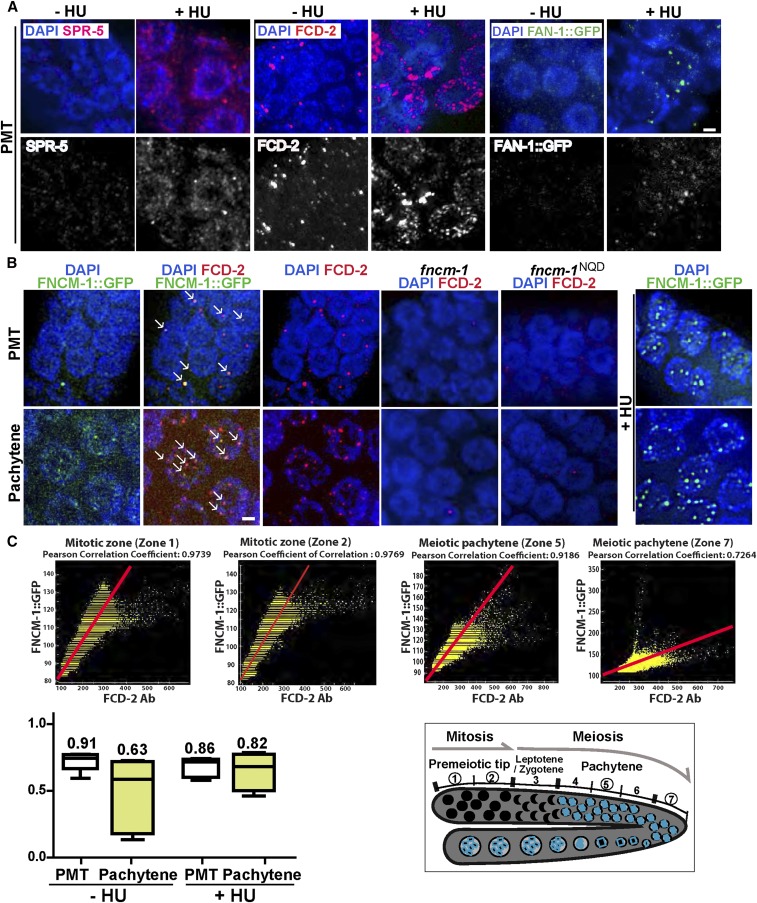
Figure 4.
Proteins in the FA pathway and the histone demethylase SPR-5 display a dynamic localization upon HU treatment and colocalize. (A) Immunolocalization of SPR-5, FCD-2, and FAN-1::GFP (FAN-1::GFP was detected with an anti-GFP antibody) upon 3.5 mM HU treatment in the mitotically dividing germline nuclei (PMT). The localization pattern of SPR-5 and of the FA pathway components FCD-2 and FAN-1 is altered in response to replication stress (+HU). (B) Immunolocalization of FNCM-1::GFP and FCD-2 in the PMT. FNCM-1 and FCD-2 colocalize on chromatin-associated foci (indicated by →) in the absence of any stress (−HU; left panels). Panel on the right shows that FNCM-1 relocalizes in response to replication stress (+HU), changing from a more diffuse to a more focal localization. The dispersed FNCM-1::GFP signal was not detected in control wild type (Figure S2). Bars, 2 µm. (C) Top: Graphs showing Pearson colocalization correlation coefficient values indicate higher colocalization levels between FCD-2 and FNCM-1::GFP starting at the PMT and slowly decreasing throughout meiosis (zones 1 and 2 = mitotic zone; zone 5 = midpachytene; zone 7 = late pachytene). Bottom left: Mean numbers of Pearson colocalization correlation coefficient values between FCD-2 and FNCM-1::GFP for both mitotic (PMT) and meiotic (pachytene) zones with or without HU exposure. n > 5 gonads. A value of 1 indicates that the patterns are perfectly similar, every pixel that contains Cy3 (FCD-2, red) also contains GFP (FNCM-1::GFP, green); while a value of −1 would mean that the patterns are perfectly opposite, every pixel that contains Cy3 does not contain GFP and vice versa. Bottom right: Diagram of the C. elegans germline indicating the mitotic (zones 1 and 2) and meiotic stages (zones 5 and 7) represented in the top panel.