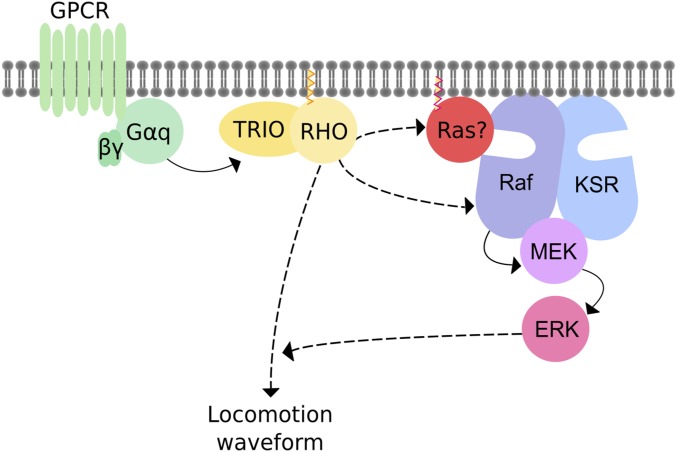
Figure 6.
Model for Gq-Rho-ERK signaling. Gq directly activates Trio and Rho (solid arrow) (Lutz et al. 2007). The core ERK cascade acts either downstream of Rho or in parallel (dashed arrows) to modulate locomotion behavior. ERK activation occurs independently of the extracellular growth factor LIN-3, its receptor LET-23, or Ras/LET-60. It is possible that Raf/LIN-45 is activated by a Ras family member other than the canonical worm Ras/LET-60. Our model suggests that Gq-Rho signaling regulates the worm waveform by acting cell autonomously in head acetylcholine neurons in an ERK-dependent pathway. By contrast, we propose that Gq-Rho signaling regulates synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction by acting in an ERK-independent pathway, possibly in the ventral cord motorneurons themselves.