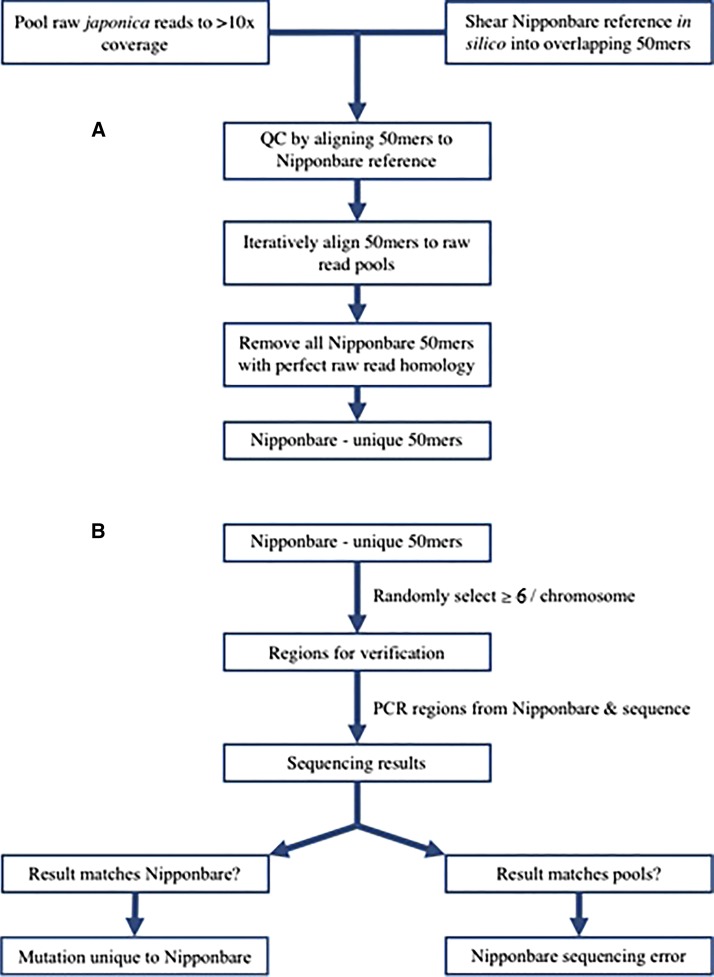
Figure 1.
Flow chart depicting the steps taken in finding recent mutations in Nipponbare via comparison to pools of other japonica rice accessions. (A) Candidate Nipponbare-specific 50-bp oligomer (50mer) discovery. First, sequence data from japonica accessions were pooled to ∼10× coverage per pool and Nipponbare was sheared in silico to create overlapping 50mers. Next, iterative alignments were conducted between the Nipponbare 50mers and the japonica pools, and all Nipponbare 50mers with perfect homology to the japonica pools were removed from consideration, yielding 50mers unique to the Nipponbare line. (B) Resolution of candidate Nipponbare-specific 50mers between sequencing error and de novo mutation possibilities. Random selection of at least six Nipponbare-specific 50mers per chromosome was conducted to identify potential changes across the genome. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Sanger sequencing of PCR products were performed on the selected Nipponbare 50mers, followed by classification of either a mutation unique to Nipponbare or a Nipponbare sequencing error.