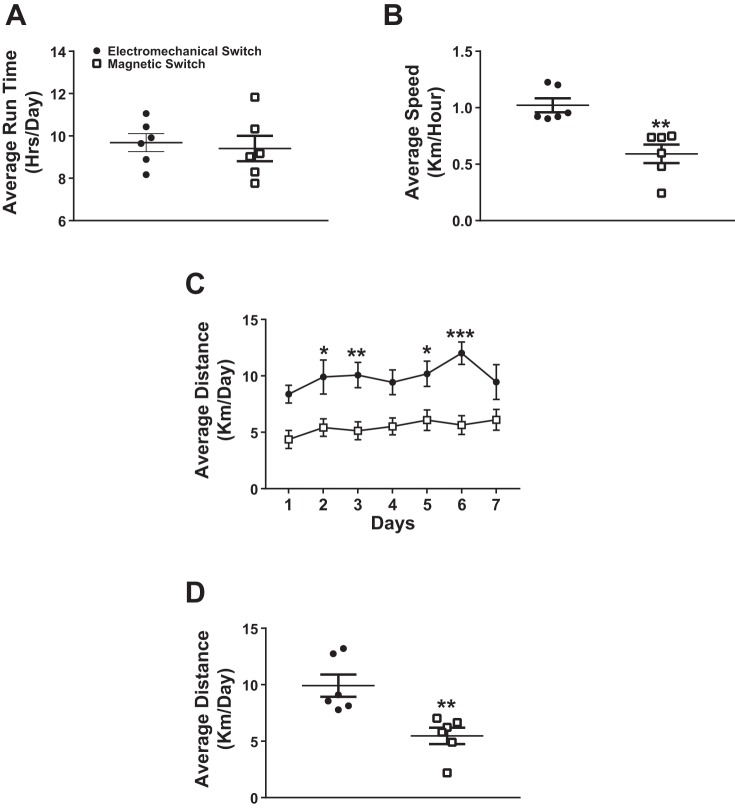
Fig. 3.
A: the average run time (h/day) was not significantly different between electromechanical switch wheel cages or magnetic switch wheel cages (n = 6). B: the average speed (km/h) was significantly reduced in the cages with the magnetic switch (n = 6). C: average daily run distance (km/day) is shown for 7 days. Mice in the electromechanical switch wheel cages ran significantly more than those in the magnetic switch wheel cages (n = 6). D: a summary graph of average daily run distance (km/day) is shown (n = 6). A two-tailed t-test was performed to compare the effect of electromechanical and magnetic switch wheel cages on run time, average speed, and average distance (*P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01). A two-way ANOVA was employed to compare the average daily distance between the 2 cage types (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).