Figure 1.
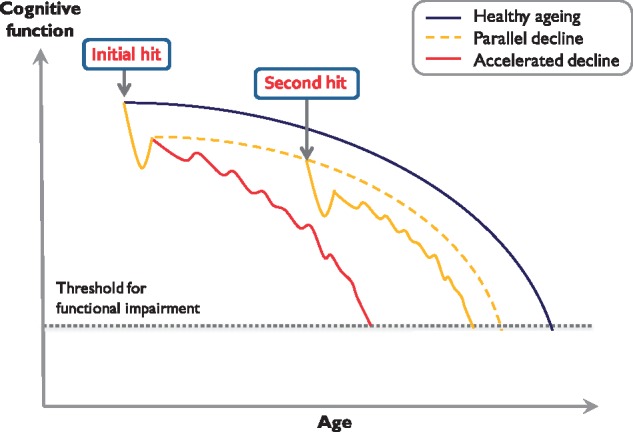
Trajectories of cognitive decline with ageing. The schematic illustrates how cognitive function in people with epilepsy might decline compared to healthy ageing (blue). One model proposes that an initial brain insult (‘initial hit’) leads to cognitive decline in epilepsy patients simply running parallel to but below the normal trajectory (dashed yellow). These individuals start from lower cognitive performance and also reach the threshold for functional impairment or dementia earlier. An alternative model is that while an initial hit might be a neurodevelopmental disorder or traumatic brain injury, subsequent development of epilepsy is in effect a ‘second hit’, which leads to further deviation from the normal trajectory (solid yellow). A third proposal is that, with increasing time, the trajectory of cognitive decline in people with epilepsy deviates further from that in healthy individuals leading to accelerated cognitive ageing (red). Inspired by a figure used by Breuer et al. (2016).
