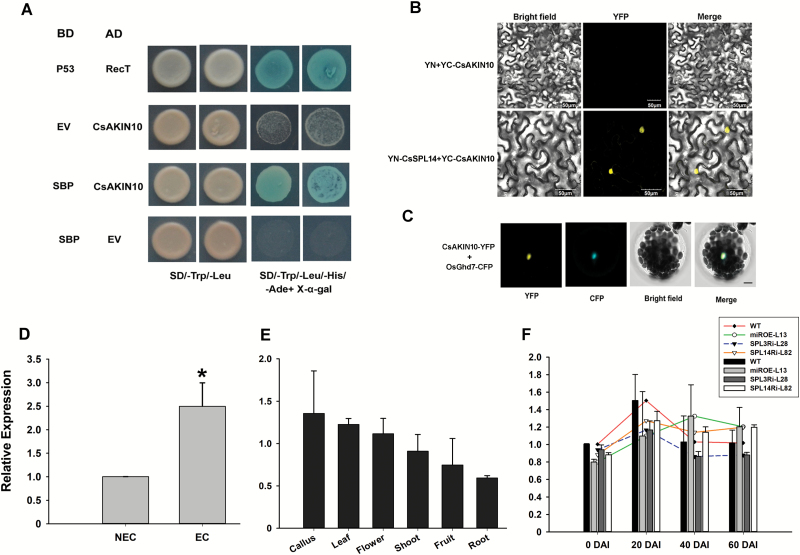
Fig. 6.
Identification of the CsSPL14-interacting protein. (A) The interaction between CsAKIN10 and CsSPL14 verified by yeast two-hybrid assays. Clones grown on synthetic drop-out selection medium that lacked Trp and Leu (SD/–Trp/–Leu) were detected by synthetic drop-out selection medium that lacked Trp, Leu, His, and Ade (SD/–Trp/–Leu/–His/–Ade) with X-α-gal. Co-transformation of BD-p53 and AD-RecT was used as the positive control. EV, empty vector. (B) CsAKIN10 was confirmed to interact with full-length CsSPL14 by BiFC assays. The construct of CsSPL14 fused with the N-terminal of YFP was co-infiltrated with CsAKIN10 fused with the C-terminal of YFP into tobacco leaves. The co-infiltrated leaves were photographed after 3 d. (C) Sub-cellular localization analysis of CsAKIN10. The CsAKIN10-YFP construct was co-transformed with OsGhd7-CFP, a positive control for nuclear localization, into Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts. The images were captured under yellow (YFP) and cyan fluorescence (CFP), and bright light, and the merged image is also shown. Scale bar = 7.5 µm. (D) Expression levels of CsAKIN10 in non-embryonic callus (NEC) and embryonic callus (EC) in ‘Valencia’ sweet orange, which has high SE competence. Statistical significance was determined by a t-test, * P<0.05. (E) Expression levels of CsAKIN10 in different tissues of ‘Valencia’. (F) Expression levels of CsAKIN10 in miR156 overexpression and CsSPL3 and CsSPL14 RNAi callus lines during SE induction in Fortunella hindsii. miROE-L13, miR156 overexpression line; SPL3Ri-L28, CsSPL3 RNAi line; SPL14Ri-L82, CsSPL14 RNAi line. DAI, days after SE induction.