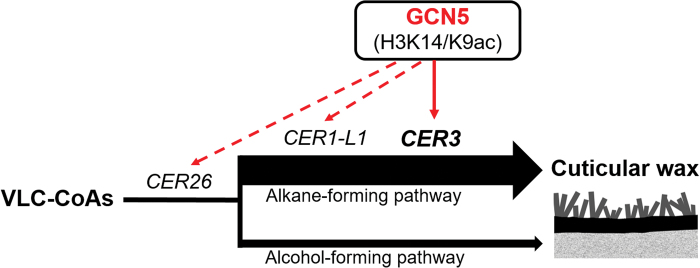
Fig. 7.
A model for the regulation of stem cuticular wax synthesis by GCN5-associated acetylation in Arabidopsis. As the wax precursors, the very-long-chain acyl-CoAs (VLC-CoA) can be processed through the alcohol-forming pathway and alkane-forming pathway, which yield 17~18% and 80% of the total cuticular wax mixture, respectively. Solid black arrows represent the cuticular wax biosynthesis pathway. The arrows from GCN5 indicate positive transcriptional regulation by GCN5 via H3K9/14ac modifications. GCN5 targets are marked at the positions where the enzymes they encode are required. CER3 is a key cuticular wax biosynthetic enzyme that catalyses the alkane-forming pathway in Arabidopsis stems (solid arrow), whereas CER26 and CER1-L1 might partially contribute to the total wax load but they were not verified functionally in this study (dashed arrows).