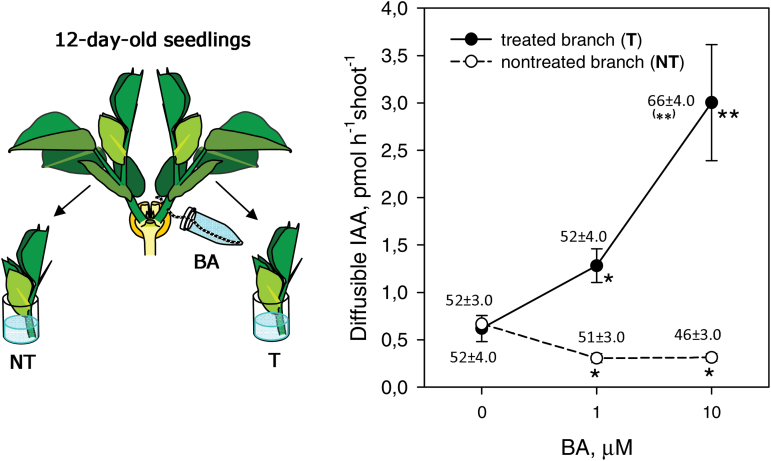
Fig. 3.
Effects of 6-benzylaminopurine (BA) treatment on the IAA export activity of shoots of 12-day-old, 2-B pea seedlings. BA was supplied into the vascular stream of one shoot (treated shoot; T). NT, non-treated shoot. A schematic of the experimental set-up is shown on the left. 2-B plants were prepared as for Fig. 1. For vascular supply, a thread submerged in 1.5 ml of 0, 1, or 10 µM BA solution (all containing 0.1% DMSO) was passed with a needle through the stem of one shoot at its base. Two days later, the IEA of T and NT shoots was determined by collecting 2 h diffusates from excised shoot tips into distilled water and subjecting the diffusates to ELISA. For each treatment, the amount of IAA measured in 5–6 diffusate samples pooled from five shoot tips was correlated with the average weight of corresponding shoot tips using linear regression (SigmaPlot 11 for Windows 7). IEA values estimated as diffusible IAA in the shoot tips with a standard weight of 45 mg were calculated using the linear regression equations (±SE). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences compared with control (0 µM BA): *P<0.05, **P<0.01. The fresh weights of shoot apical buds were measured at 12 days (2 days after treatments) and are shown above the points as mg per bud ±SE (n=30); **P<0.01.