Figure 3.
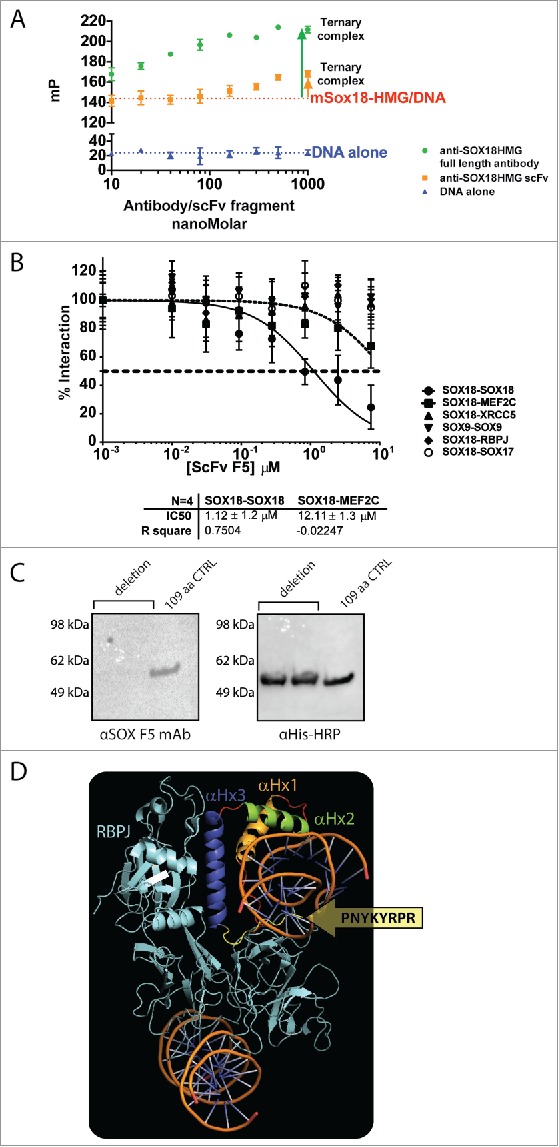
F5 scFv and mAb binding does not compete with DNA and selectively disrupts SOX18 homodimerization. A. Fluorescence polarisation-based measurement of F5 mAb concentration-dependent binding with 109-aa Sox18 fragment used for phage library affinity screening, denotes the formation of a ternary “DNA-Sox-mAb” complex. Despite binding to the HMG domain or in its vicinity, the F5 mAb does not compete with DNA binding to Sox18 HMG-box. Experimental data used for the fitting were obtained from independent triplicates. B. Representative ALPHA-Screen concentration-response curve for SOX18 Protein-Protein Interaction disruption by F5 scFv. Data shown are mean ± SEM. ALPHAScreen was performed as previously described.38,39 The assay for disruption of protein-protein interaction (IC50) was conducted by expressing the protein pairs in Leishmania tarentolae cell-free extract and incubating with a dilution range of tested scFv (0.01 to 7.5 µM) for 1h. Percentage of interaction was calculated as: from 3 independent experiments. C. F5 MAb does not bind to the 101-aa YRPRRKKQ deletion mutant of 6HIS-MBP-SOX18-109 (Left panel, lanes 1 and 2), compared to unchanged 109-aa control in lane 3. The right panel corresponds to expression controls with HRP-coupled anti-His tag Mab. D. Docking of the SOX18/DNA structure 24 into the structure of the Notch transcription complex. To investigate possible protein-protein interaction sites of SOX18, we used in silico protein-protein docking, in combination with MD simulations, to build a complex model of SOX18/DNA with its protein partner RBPJ. For RBPJ we used the X-ray crystal structure of a section of the human Notch transcription complex, elucidated in 2012.23 This section contains the ankyrin (ANK) repeat domain, the RBPJ-J-associated molecule (RAM) domain of the Notch intracellular domain, bound to coactivator MAML1, and the transcription factor RBPJ bound to its consensus DNA. Docking the SOX18/DNA structure into the structure of this Notch transcription complex with subsequent MD simulation for optimization resulted in a RBPJ/SOX18 interaction mediated by the HMG domain. The interaction between SOX18 and RBPJ (cyan) is provided by the C-terminal part of α-Helix 3 depicted in purple (residues Gln138, Arg141, Asp142, and His143) and was refined to exclude amino acid residues from the C-terminal tail of the HMG domain part of F5 Mab epitope.
