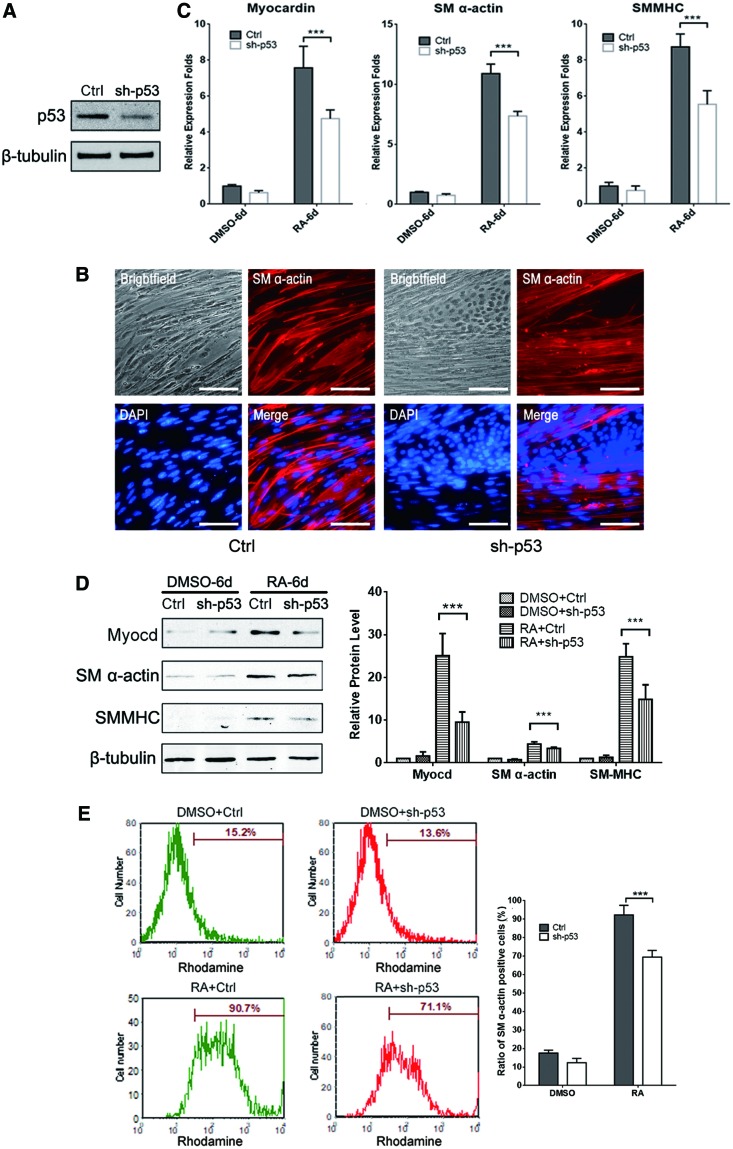
FIG. 2.
Suppression of p53 by shRNA attenuates SMC differentiation from ESCs. (A) Knocking down of p53 mRNA reduced its protein expression. (B) Representative immunofluorescence staining images from mESCCtrl and mESCsh-p53 differentiation into SMC by 10 μM RA treatment for 9 days. (C) qPCR and (D) western blotting assay demonstrated that downregulation of p53 attenuated SMC differentiation by decreasing the expression of SMC markers: Myocardin, SM α-actin, and SMMHC. β-tubulin was used as the loading control and the quantitative analysis of relative protein levels from western blotting was demonstrated with bar plot (the right panel of D, ***P < 0.05). (E) FACS assay revealed that the proportion of SM α-actin-positive cells was significantly reduced from 90.7% to 71.1% by shRNA-mediated p53 knockdown in RA-induced mESC/SMC differentiation (left), and the statistical result presented with bar plot (right, ***P < 0.05). FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; SMMHC, smooth muscle myosin heavy chain. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/scd