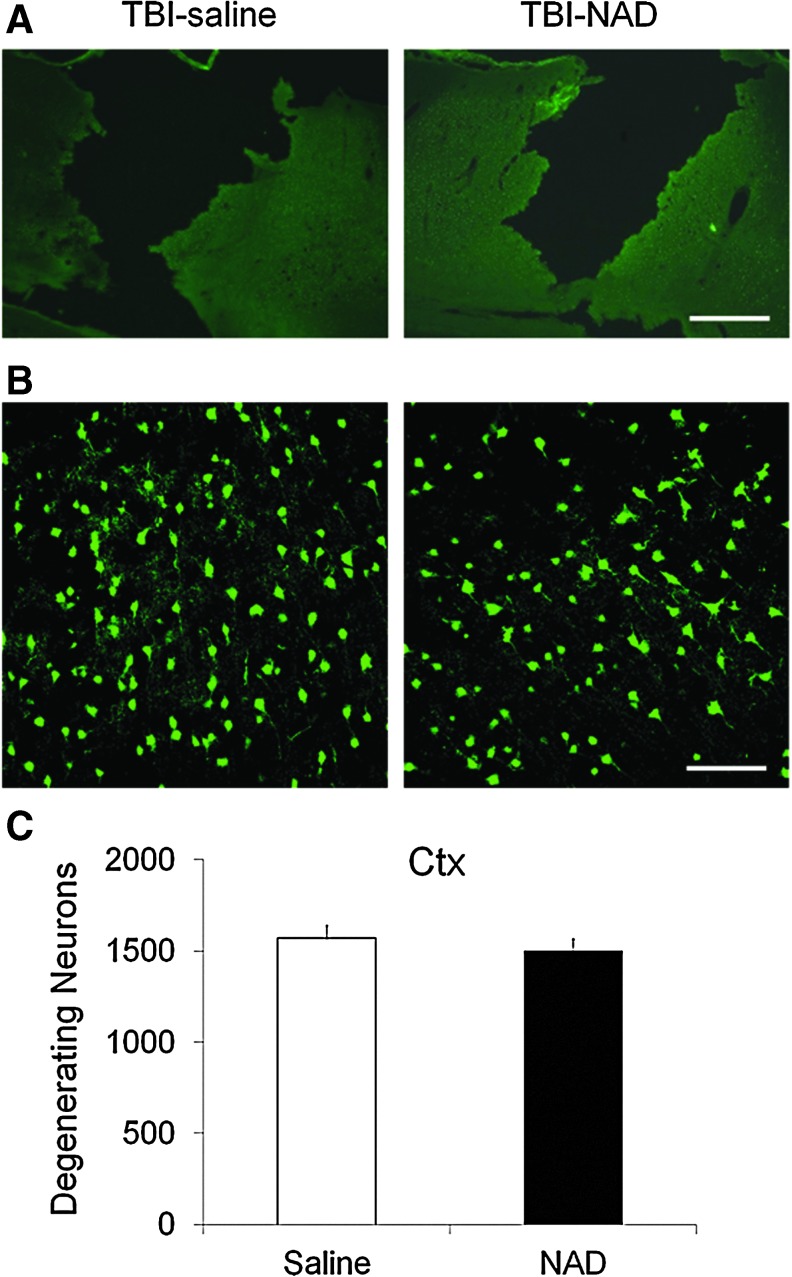
FIG. 1.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI)-induced cortical neuronal death is not prevented by intranasal administration of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). (A) TBI produced a hemisphere-shaped zone of necrosis. These low-magnification images show a loss of cortical tissue throughout the impact zone. Cortical tissue loss is almost identical in the saline-treated (TBI-saline) and NAD+-treated groups (TBI-NAD; scale bar=500 μm). (B) TBI induced severe neuron death (Fluoro-Jade B [FJB]-positive neurons) in the peri-lesional cortical impact area at 24 h after cortical impact. Confocal fluorescence images show several FJB-positive neurons in the cortex (Ctx) at 24 hours after TBI. Intranasal treatment with NAD+ provided no protective effects against cortical neuronal death (scale bar=100 μm). (C) Bar graph shows the quantified neuronal degeneration in the cortex. The number of FJB-positive neurons was not statistically significantly different in saline-treated and NAD+-treated animals. Color image is available online at www.liebertonline.com/neu