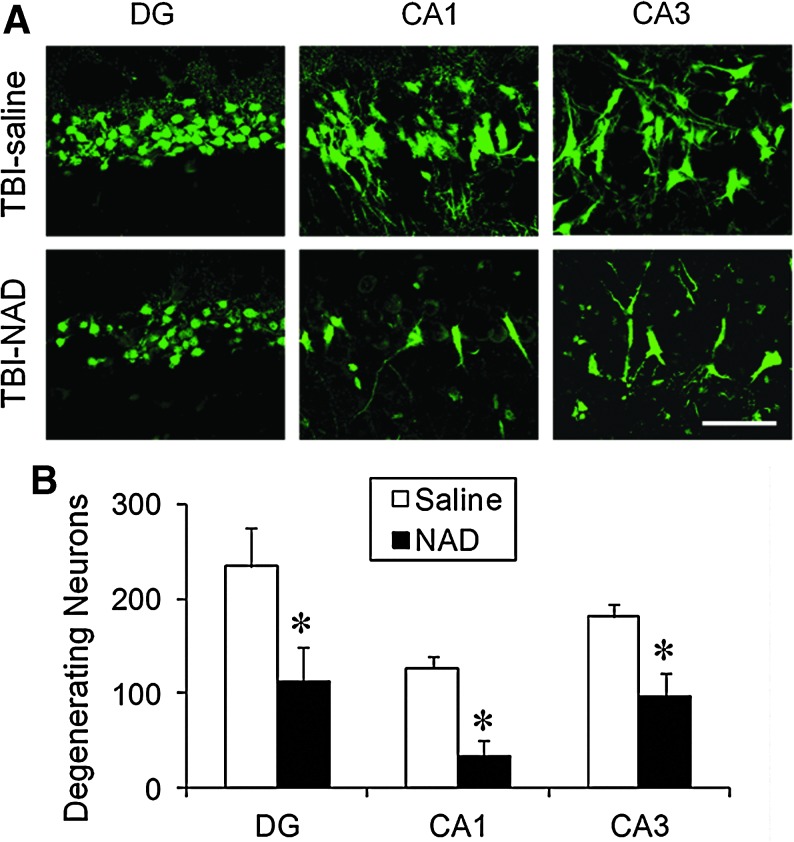
FIG. 2.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI)-induced hippocampal neuronal death is prevented by intranasal administration of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). (A) Confocal fluorescence images show neuronal death in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG), CA1, and CA3, at 24 h after TBI. A significant number of FJB-positive neurons (green-colored neurons) were observed in saline-treated (TBI-saline) rats after TBI. The number of Fluoro-Jade B (FJB)-positive neurons was significantly reduced by intranasal administration of NAD+ (TBI-NAD; scale bar=50 μm). (B) Bar graph showing the quantified degree of neuronal degeneration in the ipsilateral hippocampus. Data are mean±standard error of the mean; n=6 each group; *p<0.05 compared with the saline-treated group. Color image is available online at www.liebertonline.com/neu