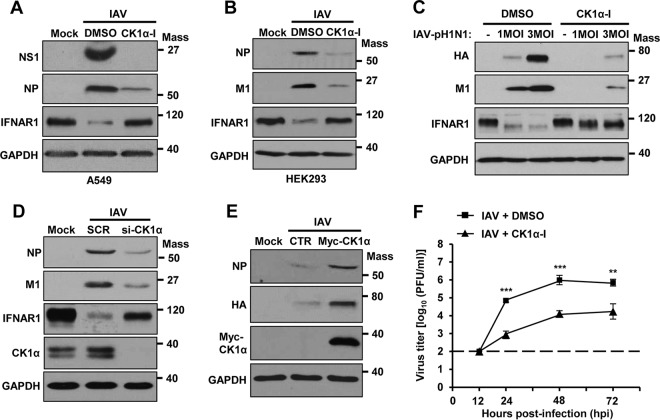
FIG 8.
CK1α regulates IAV propagation. (A and B) A549 cells (A) or HEK293 cells (B) were pretreated with CK1α-I (5 μM) or solvent (DMSO) 1 h before infection with IAV at an MOI of 1. At 24 hpi, the levels of NS1, NP, M1, IFNAR1, and GAPDH were analyzed by Western blotting. (C) HEK293 cells were pretreated with CK1α-I or DMSO for 1 h and then infected with IAV-pH1N1 at the indicated MOIs. The levels of HA, M1, IFNAR1, and GAPDH were detected. (D) HEK293 cells were transfected with siCK1α or SCR. At 24 h posttransfection, the cells were infected with IAV at an MOI of 1. Western blot analysis was performed 24 h postinfection to assess the levels of NP, M1, IFNAR1, CK1α, and GAPDH. (E) HEK293 cells were transfected with a control vector or plasmid encoding Myc-tagged CK1α. At 24 h posttransfection, the cells were infected with IAV at an MOI of 1 for an additional 24 h. The levels of NP, HA, Myc-CK1α, and GAPDH were detected by Western blotting. (F) A549 cells were treated with solvent (DMSO) or CK1α-I and infected with IAV at an MOI of 0.001. At 12, 24, 48, or 72 hpi, the titers of infectious IAV in the supernatants of the cultures were assessed by plaque assay on MDCK cells. Each data point represents the mean of samples generated from three independent experiments. The data represent means ± SD (**, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001). Mass, molecular mass (kilodaltons).