Figure 4.
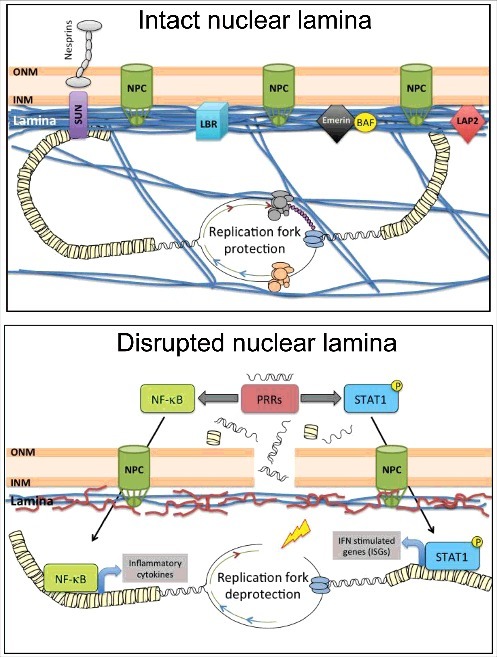
Model of progerin-induced activation of a cell intrinsic IFN-like response. Nuclear lamins and lamin-associated proteins help maintain nuclear architecture and integrity, and genome stability. Hallmarks of progerin-expressing cells include nuclear morphological abnormalities, DNA repair defects, and telomere dysfunction, leading to DNA damage accumulation and premature senescence. In addition, progerin expression hinders replication fork progression, causing replication stress. We propose that replication stress and DNA damage accumulation generates immunogenic nucleic acids that leak outside the nucleus. This “false alarm” of pathogen invasion activates PRRs, including cGAS and STING, and downstream NFkB and STAT1 pathways, which together drive an IFN-like response. Treatment with vitamin D, as well as other compounds such as farnesyltransferase inhibitors and rapamycin, all-trans retinoic acid, and remodelin, rescue replication defects and reduce DNA damage. These improvements are accompanied by repression of the STAT1/IFN-like response, suggesting that this pathway contributes to cellular decline in progeria.
