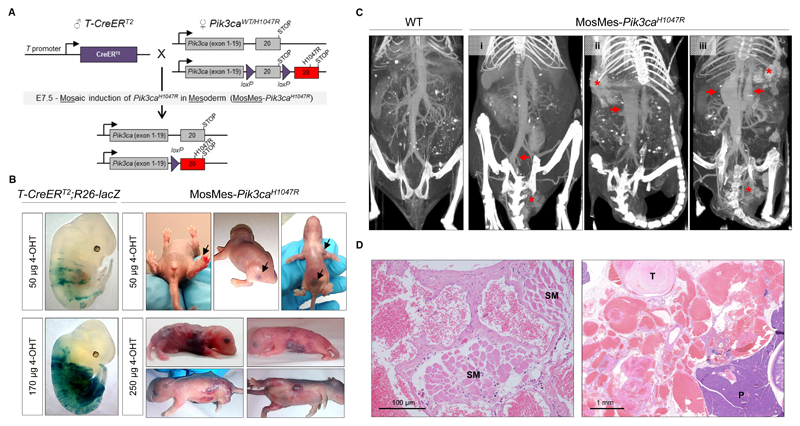
Figure 1. Mosaic expression of Pik3caH1047R in embryonic mouse mesoderm induces vascular malformations.
(A) Genetic strategy for mosaic Pik3caH1047R induction in the embryonic mesoderm. T-CreERT2 mice were crossed with Pik3caWT/H1047R mice that have a germline Pik3ca allele with a conditional H1047R mutation in exon 20. Mosaic recombination in the mesoderm was induced by a single intra-peritoneal injection of a low dose of 4-OHT to pregnant mice at E7.5. (B) Left, E12.5 T-CreERT2;R26-lacZ mouse embryos from pregnant mice injected with the indicated dose of 4-OHT at E7.5 and stained for β-galactosidase (β-gal) activity. Right, Representative photographs of P1-P5 MosMes-Pik3caH1047R pups with congenital vascular malformations (indicated by arrows in the top panel), born to pregnant mice injected with the indicated 4-OHT dose at E7.5. (C) CT-A scans of adult mice four hours after intravenous injection of gold nanoparticles. The WT mouse (left) shows normal vascular anatomy, whereas MosMes-Pik3caH1047R mice display dilatation of the left common iliac vein (arrow) and VM in the urogenital area (asterisk) (mouse #1); subcutaneous VM (asterisk) and dilatation of the inferior vena cava (arrow) (mouse #2); subcutaneous and urogenital VMs (asterisks) and dilatation of the inferior vena cava and portal vein (arrows) (mouse #3). (D) Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections of subcutaneous (left) and deep mesenteric (right) VMs in MosMes-Pik3caH1047R mice, showing abnormal, enlarged, and irregular vascular channels, most containing blood and organising fibrin thrombi (T), some interposing between skeletal muscle (SM) and other tissue structures. No cytological atypia was observed. (P, pancreas).