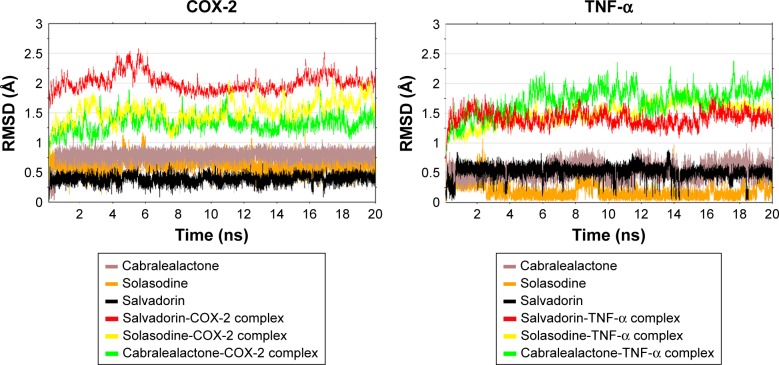
Figure 7.
Simulation results of protein-ligand complexes.
Notes: RMSDs during MD simulation of COX-2 and TNF-α of protein-ligand complexes. The RMSDs are plotted as a function of time in 1 ns of the protein backbone of COX-2 and TNF-α with docked ligands during MD simulation at 20 ns. Histopathological findings confirm carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) induces liver injury by binding to the extracellular receptor which results from the toxic metabolites of CCl4 causing centrilobular hepatic necrosis and steatosis that disturb the essential cellular processes. CCl4 is biotransformed by cytochrome P450 system in the hepatic microsomes, producing trichloromethyl free radical (CCl−°3) that reacts with cellular molecules and perturb the cellular processes. In the presence of oxygen, CCl°3 is converted to trichloromethyl peroxy radical (CCl3OO−°), resulting in oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and loss of membrane integrity. The described model of liver fibrosis indicates that macrophages progress the differentiation and proper functioning of fibroblasts, and act as potent therapeutic agent. Standardized extract of Cleome brachycarpa (cabralealactone) suppressed the activation of p53, decreased the expression level of anti-apoptotic protein Bax, and increased the expression level of apoptotic Bcl-2, which resulted in reduced cytochrome C release from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm and inactivated caspases 3 and 9. Ultimately, cabralealactone suppressed fibrosis and necrosis of the hepatocytes. Acute injection of CCl4 induces hepatocyte necrosis or apoptosis. Damaged hepatocyte release lipid antigens (represented by HSC) resulting in activation of Nk cells. The activated HSC produce a variety of pro-inflammatory cytokines, that is, TNF-α, NF-κβ, IL-6, and COX-2, contributing to hepatocyte inflammation. Treatment of hepatocyte via oral and intraperitoneal injection of standardized extracts of Solanum incanum (solasodin) and Salvadora oleoides (salvadorin) can attenuate the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines via inhibition of HSC activation and inhibition of the release of cytochrome c oxidase from the mitochondria. Molecular docking studies were carried out to assess the binding affinity of the compounds to proteins, thus mediating tumor growth.
Abbreviations: CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; IL, interleukin; MD, molecular docking; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa beta; RMSD, root mean square deviation; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha.