Fig. 4.
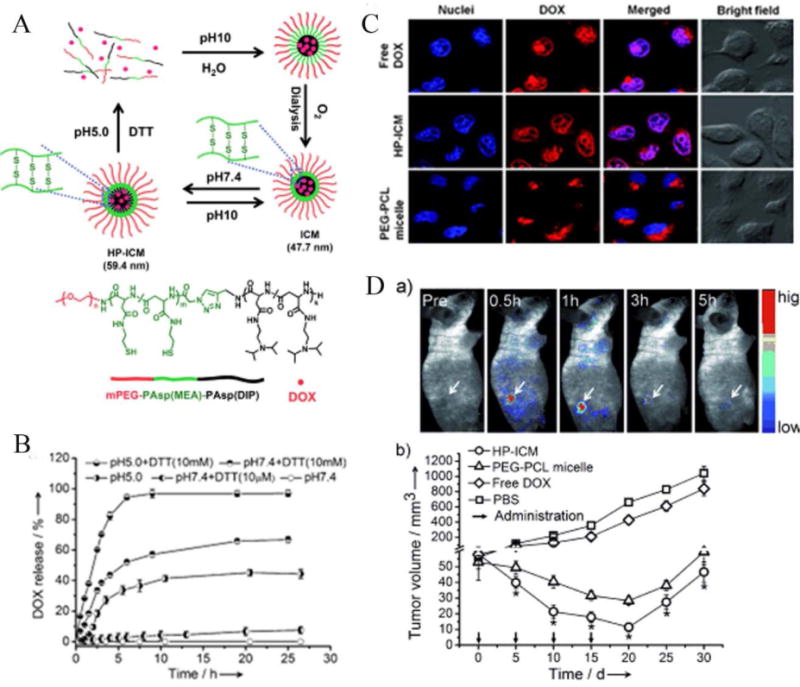
(A) Dual-sensitive interlayer-cross-linked micelles (HP-ICM) can be assembled from mPEG-PAsp(MEA)-PASM(DIP) with DOX loading at pH 7.4, and are stable up to pH 10. However, at pH 5.0 or under reducing conditions (DTT), the micelles rapidly disintegrate to release DOX. (B) Release profile of DOX from HP-ICM at various pH and reducing conditions. (C) Cellular uptake of DOX delivered as free drug, HP-ICM, and control PEG-PCL micelles. (D) Fluorescence images showing in vivo accumulation of DOX into tumor-bearing nude mice. DOX-loaded HP-ICM passively accumulate in the tumor. (a) Tumor growth inhibition is greatest when DOX-loaded HP-ICM are injected via tail vein, compared to controls (b). Reproduced with permission from Reference [73]. Copyright 2011, Wiley-VCH.
