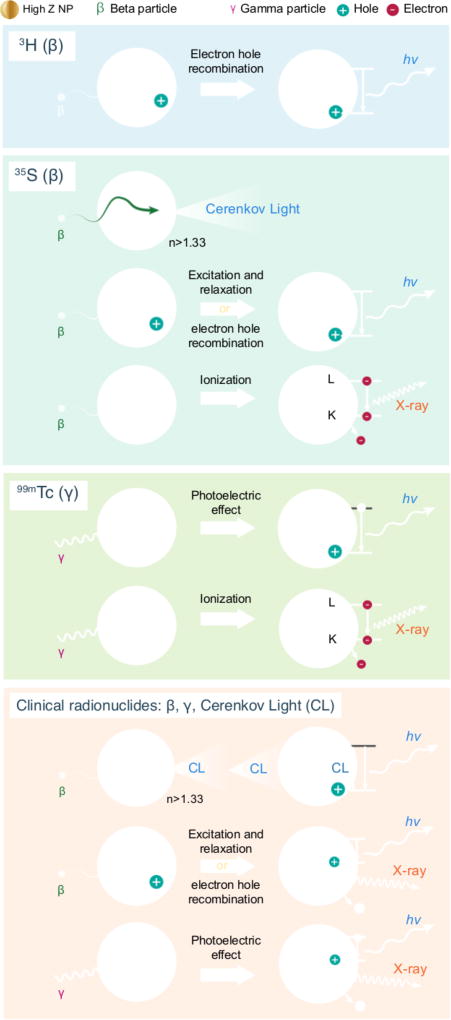
Figure 6.
Interactions between ionizing radiation and NP. Ionizing radiation interactions with NP may result in a number of emissions. Low-energy β emissions from radionuclides like 3H with TiO2 can cause electron hole recombination and resultant emission of photons. β emissions in the tens to hundreds of keV can result in numerous interactions with nanoparticles, such as Cerenkov emission within the NP, excitation or electron hole formation, or atom ionization in the NP of interest. High-energy photons, such as the 140 keV gamma from 99mTc, can result in the photoelectric effect or ionization within the NP. Clinical radionuclides such as PET tracers and radiotherapeutics, can result in the all of the aforementioned interactions along with CL interactions from the NP.