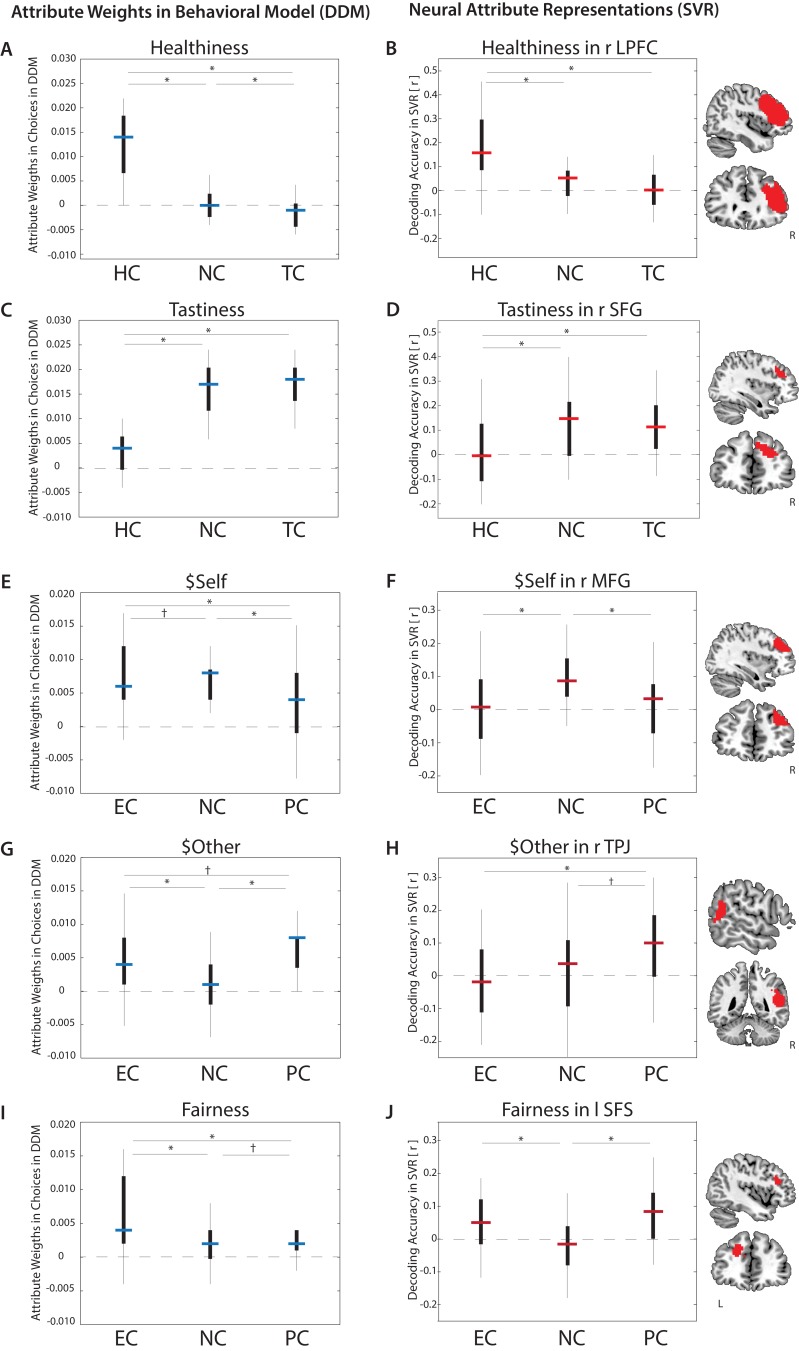
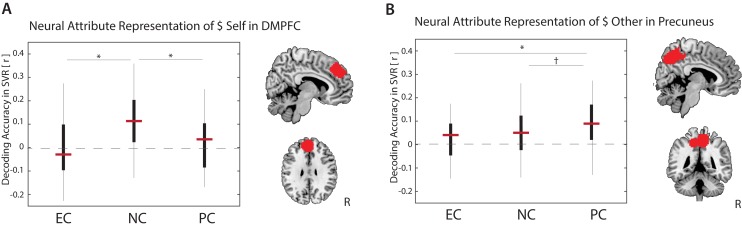
Figure 2. Goal-dependent modulation of attribute value encoding.
Behavioral weights (left column) assigned to attributes in food choices (A. Healthiness, C. Tastiness) or altruistic choices (E. $Self, G. $Other, I. Fairness) varied by regulatory goal (estimates of drift diffusion models, DDMs). Neural decoding accuracies of attribute values (right column) also varied across conditions in specific brain regions (B. Healthiness, D. Tastiness, F. $Self, H. $Other, J. Fairness) (p < 0.05, FWE corrected at cluster-level) (estimates of Support Vector Regression models, SVRs). Bars represent median estimates (blue = behavioral DDMs, red = neural SVRs; black boxes signify 25–75 percentile, lines illustrate the overall distribution), HC = Health Condition, NC = Natural Condition, TC = Taste Condition, PC = Partner Condition, EC = Ethics Condition, L = left hemisphere, R = right hemisphere, LPFC = Lateral Prefrontal Cortex, SFG = Superior Frontal Gyrus, MFG = Mid Frontal Gyrus, TPJ = Temporoparietal Junction, SFS = Superior Frontal Gyrus.