Figure 3.
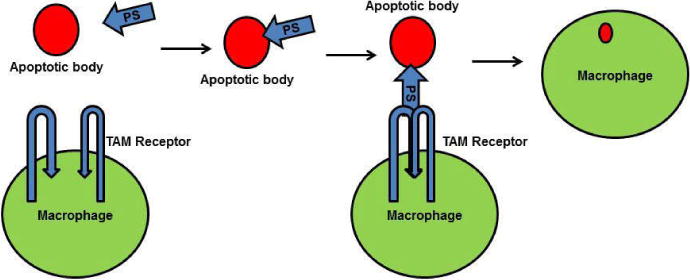
Functions of PS-TAM receptor signaling. A) The Gla domain of PS interacts with phosphatidylserine on the apoptotic cell membrane, and the SHBG domain of PS forms a crosslink with a TAM receptor on a macrophage. This crosslink promotes phagocytosis of the apoptotic cell.
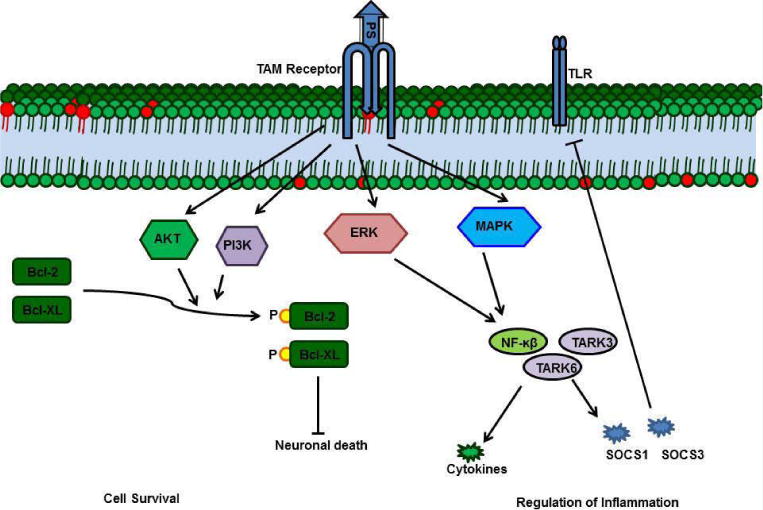
PS-TAM signaling activates the MERK/ERK pathway, which, in turn, activates NFkb, TARK6, and TARK3 to promote expression of cytokines and suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCSs). Enhanced SOCSs expression blocks Toll-like receptors. In neurons, PS-TAM signaling activates the PI3 and Akt pathways, which, in turn, phosphorylate Bcl2 and Bcl-XL; phosphorylated Bcl2 and Bcl-XL promote cell survival.
PS-Axl enhances VEGFla signaling and enhances angiogenesis in vascular smooth muscle cells, whereas PS-MER antagonizes VEGF signaling in endothelial cells.
