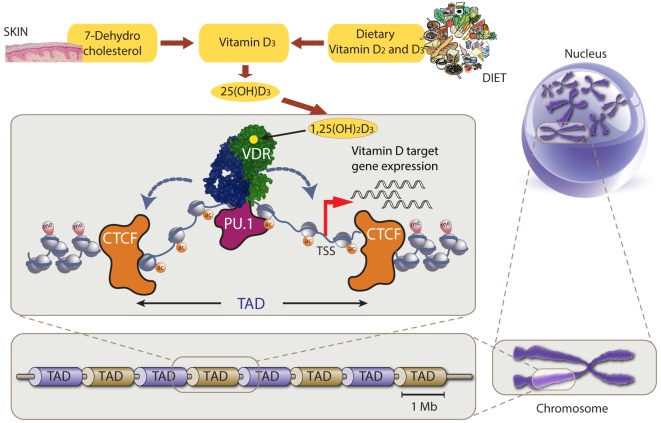
Figure 1.
Chromatin model of vitamin D signaling. Top: production of vitamin D3 and its metabolites 25(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3. Center: vitamin D receptor (VDR) (green) binds accessible genomic DNA in complex with a partner protein (RXR or others, blue). VDR’s DNA binding is supported by the pioneer factor PU.1 (purple). The genomic region that can be influenced by 1,25(OH)2D3 (via binding to VDR) is restricted by CTCF proteins (orange) defining left and right topologically associated domain (TAD) borders, i.e., only vitamin D target genes within the TAD will be stimulated to produce more mRNA copies. Bottom and right: schematic illustration of TAD size on relation to chromosomes and the nucleus.