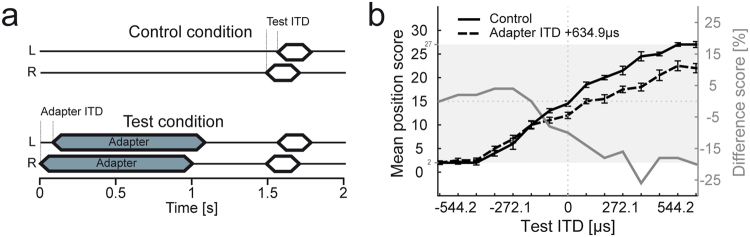
Figure 2.
Experimental designs and analyses of perceptional shift. (a) Schematic depicting a sample trial sequence to determine the intracranial perception of target tones without and with adapter. Both in the control and test condition target tones (white) were 220 ms in duration and were presented with a randomly chosen test ITD ranging from −634.9 to +634.9 µs in 90.7 µs steps. In the test condition the target tone was preceded by the adapter (1 s in duration) with a pause of 500 ms between adapter and target tone. All stimuli were presented with a frequency of 200 Hz (b) Position scores (indication of the listeners’ intracranial target tone perception, with 0 being most left and 30 being most right) without and with adapter (solid and dashed black line) as a function of test ITD for one exemplary subject (data are represented as mean over ten trials for each test ITD, ±S.E.M.). The grey shaded area depicts the individual range (i.e. range between the minimal (2) and maximal (27) mean position score for this subject). To determine the effect of a preceding adapter, the difference score (difference in position scores for each test ITD between control and test condition, normalized to the individual range) was calculated and plotted as a function of the presented test ITDs (grey solid line). Deviations from zero indicate a perceptual shift due to a preceding adapter (negative = shift to the left, positive = shift to the right).