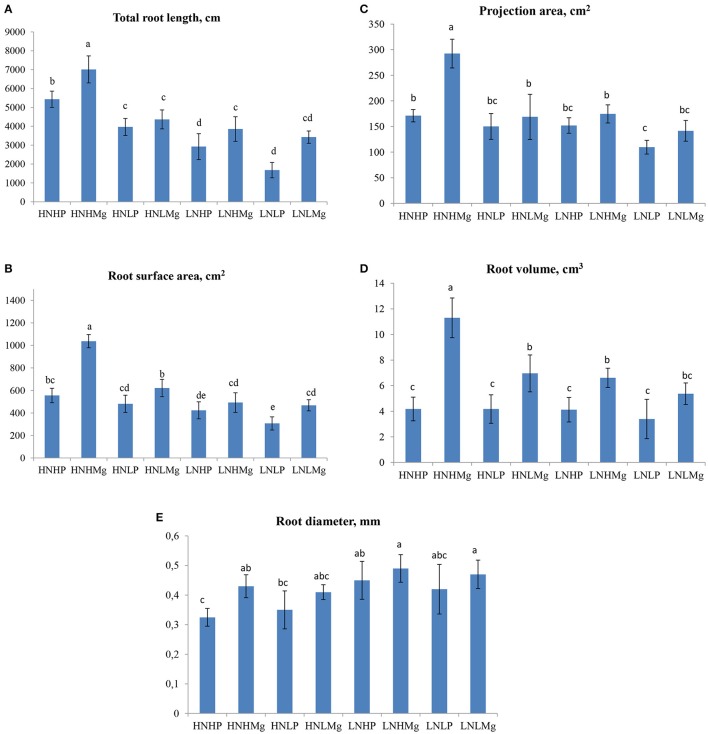
Figure 1.
Root morphological traits [total root length (A), surface area (B), projection area (C), root volume (D), and root diameter (E)] of soybeans inoculated with Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110 grown under different N, P, and Mg supplies (HNHP (N−3,000 μmol/L and P−250 μmol/L), HNHMg (N−3,000 μmol/L and Mg−1,000 μmol/L), HNLP (N−3,000 μmol/L and P−50 μmol/L), HNLMg (HNHMg (N−3,000 μmol/L and Mg−250 μmol/L), LNHP (N−300 μmol/L and P−250 μmol/L), LNHMg (N−300 μmol/L and Mg−1,000 μmol/L), LNLP (N−300 μmol/L and P−50 μmol/L), LNLMg (N−300 μmol/L and Mg−250 μmol/L). Plants were grown for 45 days under hydroponic conditions. Columns represent means for five plants (N = 5), with standard error bars, and different letters indicate significant differences between treatments at P < 0.05 (Tukey's t-test).