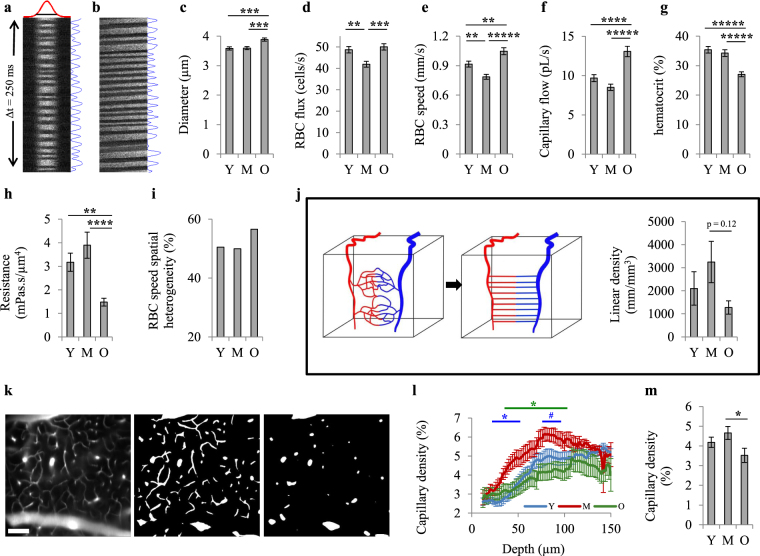
Figure 4.
Capillary blood flow. (a) A representative space-time image from perpendicular scans. The image was averaged in vertical direction and fitted with a Gaussian function (top) to estimate the capillary diameter. The image was also averaged in horizontal direction (right) to find the number of passing RBCs. (b) A representative space-time image from longitudinal scans. RBC velocity was calculated from the angle of dark streaks. The image was rotated by this angle and averaged (right) to find the number of passing RBCs. (c–g) Capillary diameter (c), RBC flux (d) and RBC speed (e) were obtained from space-time images. Capillary volumetric flow (f) and hematocrit (g) were calculated from diameter, flux and speed (Y, n = 242; M, n = 252; O, n = 278 capillaries). (h) Capillary resistance was estimated from diameter and hematocrit. (i) Spatial heterogeneity (defined as the coefficient of variation) of RBC speed. (j) For the mice that both flow in large vessels and capillary flow were measured over the same region (Y, n = 8; M, n = 7; O, n = 8 mice), capillary linear density was estimated (right) by simplifying the capillary network architecture as straight tubes with uniform length and diameter connecting an arteriole to a venule (left). (k) Microvascular angiograms were used to directly obtain the capillary density. Left: an en face slice at the depth of ~80 µm (scale bar: 100 µm). Middle: binarization of the left image. Right: the same as middle image, but processed with a median filter to remove the fine structures (capillaries). (l) Capillary density (volume%) versus depth obtained from angiograms by subtracting the density of large vessels from total vascular density. The blue * (or #) represents statistically significant (or nearly significant) differences between Y and M. The green * represents statistically significant differences between M and O. (m) Average capillary density through the depth of 0–150 µm (Y, n = 18; M, n = 15; O, n = 16 angiograms). Results are presented as mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was calculated using ANOVA followed by Tukey HSD post hoc test. *****p < 0.00001, ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, #p-value approaches significance (p < 0.1). Y: young (8 mice), M: middle-aged (7 mice), O: old (8 mice).