Fig. 5.
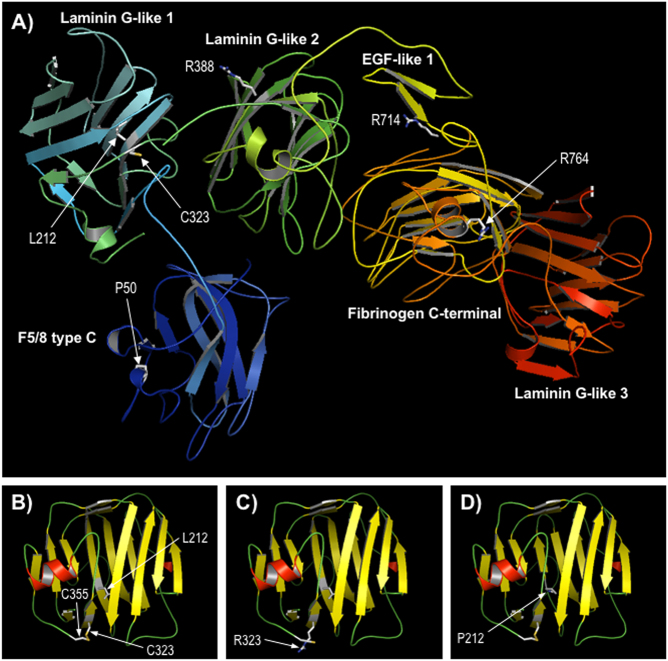
Comparative modelling of CASPR. a Predicted structure of CASPR residues 21–960. The sequence of CASPR (residues 1–1384) was modeled using the Phyre2 server; a multi-template, high-confidence model (~98% of residues modeled at > 90% confidence) was obtained for a contiguous region spanning residues 21–960, which includes most of the extracellular domain (1–1284) and includes all missense variants discussed here. The protein is shown in ribbon format coloured by secondary structure succession (N-terminal, blue to C-terminal, red); the sidechains of positions of missense variants are shown in stick format and labelled; domain annotation is taken from the InterPro database entry for CASPR (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/protein/P78357). b–d Modelling of the Laminin G-like 1 domain only (residues 174–355), based on template 3poyA, for wild-type CASPR and variants p.Cys323Arg and p.Leu212Pro respectively; protein is shown in ribbon format, coloured by secondary structure type (red, α-helix; yellow, β-strand; green, loop); the disulphide bond between cysteines 323 and 355 in B is shown by a yellow line; view is rotated compared to Fig. 4a for clarity