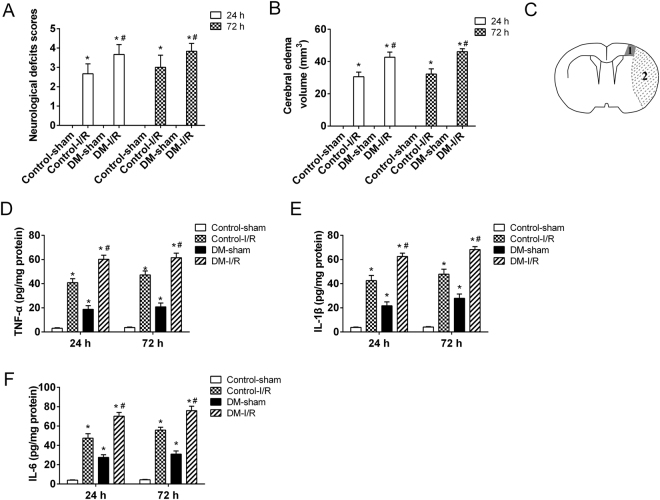
Figure 1.
Establishment of cerebral ischemic reperfusion (I/R) injury model in diabetic rats. SD rats were randomly divided into 4 groups: Control-sham, Control-I/R, DM-sham, DM-I/R. The diabetic rats (n = 12) were induced by intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ, 60 mg/kg). The another 12 rats were received the equal volume of citrate buffer. The cerebral I/R injury models in diabetic rats (DM-I/R, n = 6) were established by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). The diabetic rats were sham operated, as control for cerebral I/R injury (DM-sham, n = 6). The rats with citrate buffer received MCAO (Control-I/R, n = 6) and sham operation (Control-sham, n = 6), respectively. (A) The functional neurological deficit score was assessed and (B) the brain edema was determined at 24 and 72 hours after cerebral I/R injury. (C) A schematic of the peri-infarct area. 1: peri-infract cortex; 2: ischemic core. The secretion levels of (D) TNF-α, (E) IL-1β and (F) IL-6 in the peri-infarct cortical tissues were detected by ELISA assay. *P < 0.01 vs. Control-sham; #P < 0.01 vs. Control-I/R.