Figure 5.
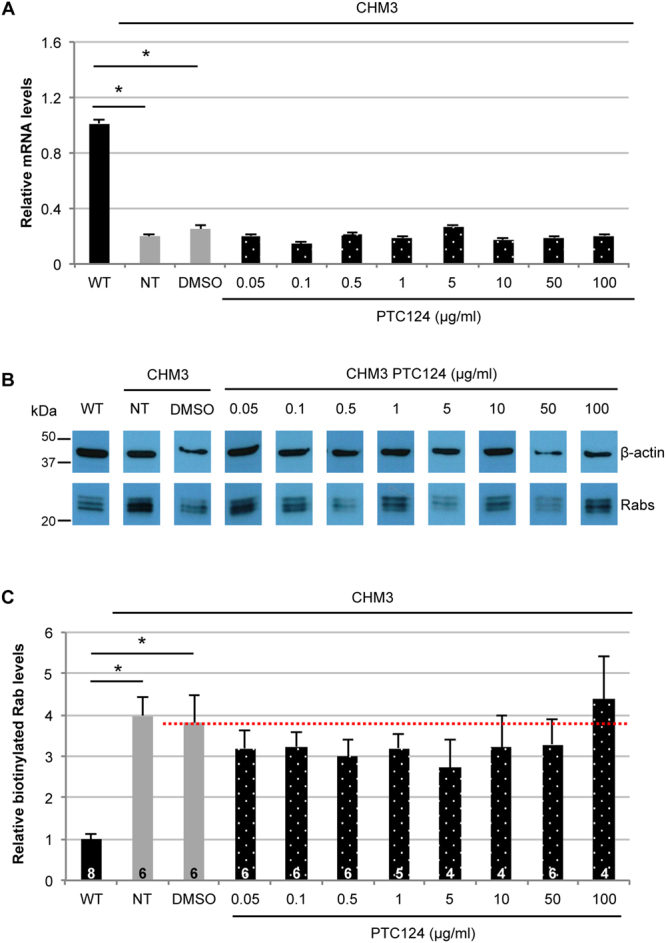
Effect of PTC124 treatment on CHM3 iPSC-derived RPE. (A) qPCR analysis of CHM mRNA levels in PTC124-treated patient iPSC-derived RPE (dotted bars). CHM transcript levels in non-treated (NT) and DMSO-treated CHM3 RPE (grey bars) are significantly lower than those of wild-type (WT; black bars) cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 3; Mann and Whitney test *p < 0.05. PTC124 treatment of CHM3 iPSC-derived RPE, regardless of the concentration used, did not significantly alter CHM transcript levels as compared to DMSO-treated cells; Kruskal-Wallis test p > 0.05. (B) A representative in vitro prenylation assay showing biotinylated Rab proteins in wild-type (WT), and in non-treated (NT), DMSO-treated or PTC124-treated CHM3 iPSC-derived RPE. β-actin serves as a loading control. Bands were cropped from the same gel. (C) Quantification of the relative biotinylated Rab levels in multiple independent assays, after normalisation to β-actin loading, shows a significant 4-fold increase in the non-treated (NT) or DMSO-treated iPSC-derived RPE of patient CHM3 (grey bars), as compared to wild-type RPE (WT; black bar). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM; n is indicated in the corresponding histogram bars; Mann and Whitney test *p < 0.05. Treatment with PTC124 results in a non-significant decrease in biotinylated Rab levels at all doses (dotted bars), with the exception of 100 µg/ml, as compared to DMSO-treated cells (red line); Kruskal-Wallis test p > 0.05.
