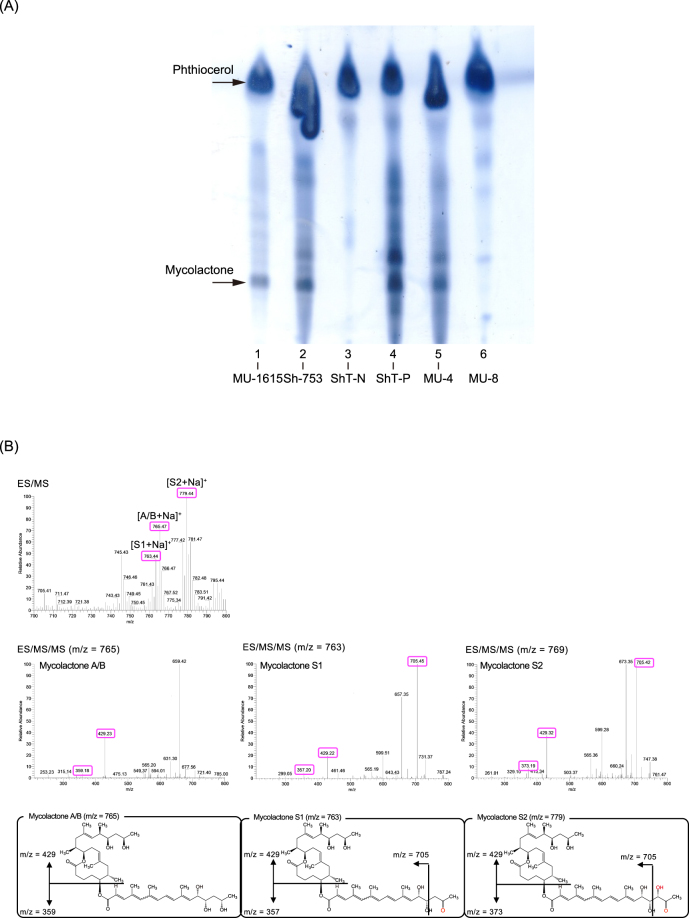
Figure 2.
Silica thin-layer chromatography and ESI/MS/MS analyses of acetone soluble lipids (ASLs) from M. ulcerans or “M. shinshuense” isolates. (A) ASLs extracted from the bacterial cell mass (CM). Samples were loaded as follows: lane 1, MU-1615 (M. ulcerans Malaysian strain, virulent); lane 2, Sh-753 (“M. shinshuense”, virulent); lane 3, ShT-N (ATCC 33728, non-pigmented colony); lane 4, ShT-P (ATCC 33728, pigmented colony); lane 5, MU-4 (M. ulcerans 97–107 African strain, virulent); lane 6, MU-8; (M. ulcerans 5143 Mexican strain, avirulent). Arrows show the position of mycolactone and phthiocerol (control lipid). (B) The ESI/MS spectrum of ASLs from the strain ShT-P detected the peaks of m/z 765.4, 763.4, 779.4 as [M + Na]+. In each MS/MS spectrum, the distinct ions were found m/z 359 and 429 for mycolactone A/B; m/z 357, 429 and 705 for mycolactone S1; m/z 373, 429 and 705 for mycolactone S2, respectively. These molecular and fragment ions were fixed the proposed structures of each mycolactone.