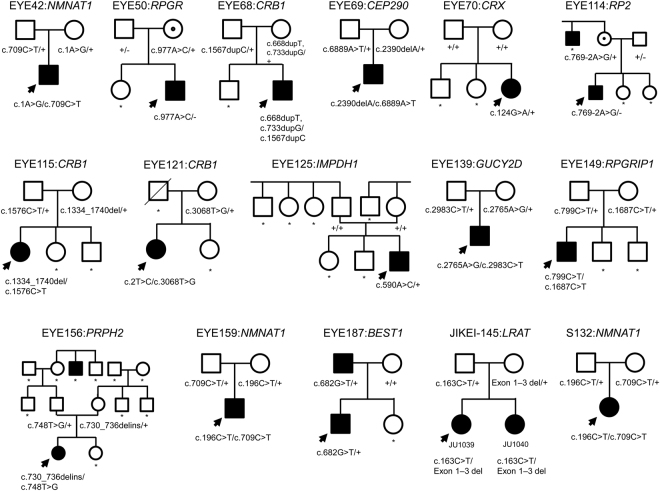
Figure 2.
Pedigrees and segregation analyses for the analysed families. The results of the segregation analyses for families EYE20, EYE55, and LCA1H have been previously reported10,11. Patient EYE68 harboured three variants, of which both p.(L223Ffs*4) and p.(A245Gfs*16) were maternally inherited, and predicted to produce transcripts likely to be targeted for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, and thus no final protein product. Both variants were thus considered to be likely pathogenic; however, this was not able to be confirmed by the present study. The parents in family EYE156 were normally sighted at the time of their examinations; however, it is possible that this may be a delayed effect of a late-onset form of retinitis pigmentosa (RP) likely to be induced as a result of their identified heterozygous variants in PRPH2, a known autosomal dominant RP-associated gene. The identification code and gene(s) relevant to each family are shown above the pedigree, and the genotype for each family member is shown below their symbol. Probands are indicated by arrows. Square, male; circle, female; black colour, disease-affected; circle with a central black dot, X-linked carrier; slashed symbol, deceased individuals; asterisk, no available DNA sample.