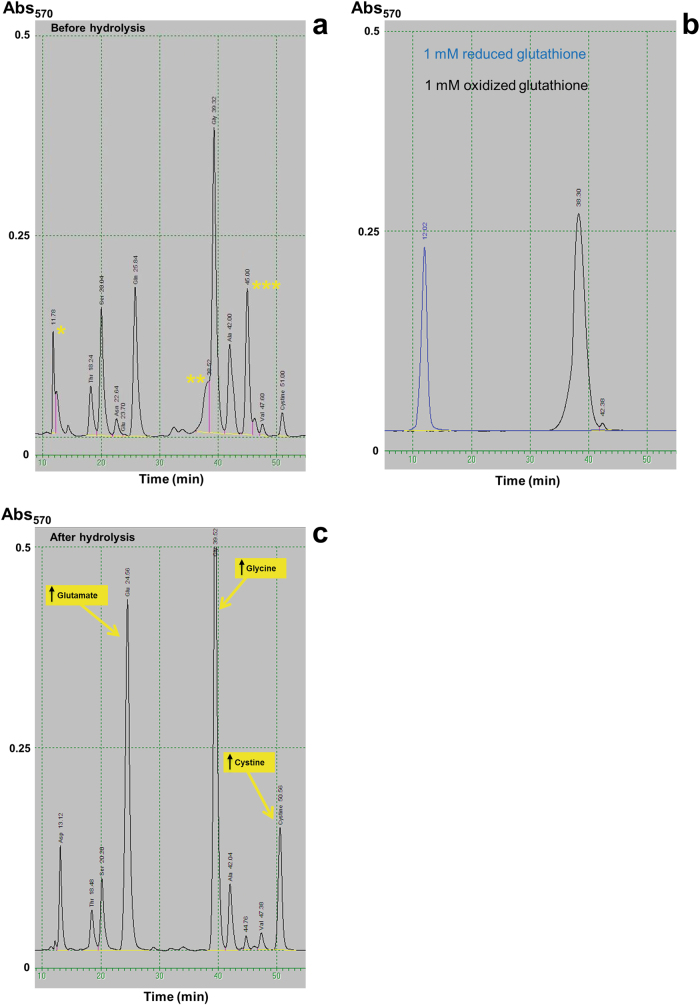
Fig. 2.
Analysis of amino acids in urine. a Direct analysis revealed the presence of three peaks of unclear identity (marked with asterisks). Two of them (* and **) have the same retention time as reduced and oxidized glutathione, respectively, as show in b. The third one (***) has a retention time consistent with a thiol derivative previously described in a patient with glutathionuria [11]. c Hydrolysis in 6 N HCl eliminates all three peaks and produces an increase of glutamate, glycine, and cystine, the expected hydrolysis products of glutathione in non-reducing conditions