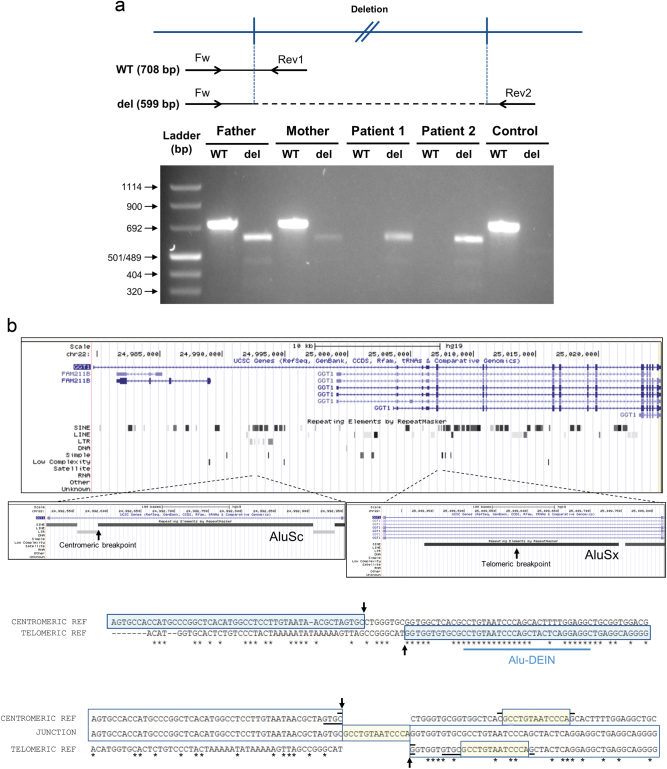
Fig. 4.
a Agarose gel electrophoresis of fragments amplified from the DNA of both patients and their parents using primers designed to give a PCR product in the absence/presence of the deletion. Upper panel: primer pair Fw-Rev1 (WT) is expected to produce a 708 bp product only in the absence of the deletion, whereas primer pair Fw-Rev2 (del) is expected to produce a 599 bp only in the presence of the deletion. Lower panel: DNA from both parents produced products with both primer pairs, indicating that they are heterozygotes for the deletion. DNA from both affected siblings produced a product only with the “del” primer pair, as expected for homozygotes for the deletion, whereas a control sample produced a product from the WT pair only. b Both breakpoints of the deletion are located in Alu elements. Upper panel: UCSC depiction of GGT1. RepeatMaster track shows abundant SINE elements in this gene. Zooming at both breakpoints shows that both are located in Alu elements. Middle panel: ClustalO alignment of the flanking regions of both breakpoints reveals substantial areas of homology, denoted by asterisks. Of special interest is the presence of a region close to both breakpoints that shares high homology to the 26 bp Alu-DEIN sequence, a recombination hotspot. The breakpoints are indicated by arrows. Lower panel: alignment of centromeric and telomeric reference sequences with the sequence obtained at the junction from patient 1. The 13 bp insertion and its two possible origins are encased in yellow. Horizontal black bars indicate putative microhomology regions. See Supplementary Figure 2 for proposed microhomology-based replication slippage and template-switching events underlying the genomic rearrangement presented here