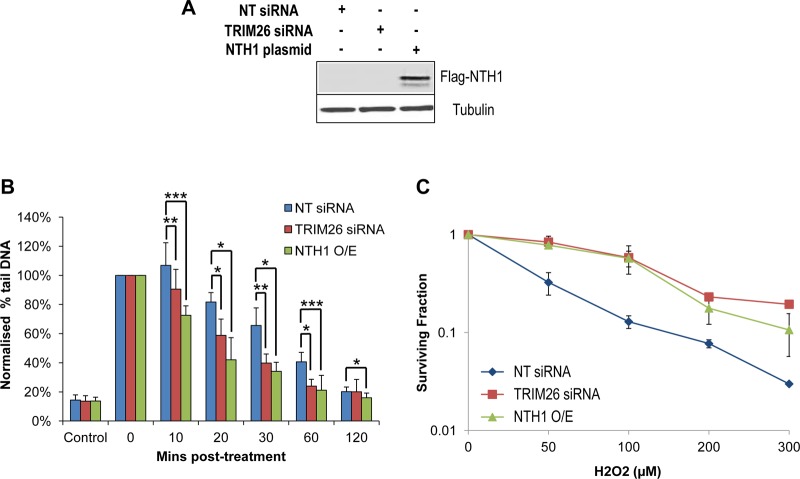
FIG 8.
Cellular sensitivity to oxidative stress is controlled by TRIM26 through NTH1 regulation. (A to C) HCT116 cells were grown in 10-cm dishes for 24 h to 30 to 50% confluence and then treated with Lipofectamine RNAiMax transfection reagent (10 μl) in the presence of 800 pmol NT siRNA or TRIM26 siRNA for 72 h. Cells were also treated with Lipofectamine 2000 transfection reagent (10 μl) in the presence of 500 ng mammalian expression plasmid for NTH1 (NTH1 O/E) for 24 h. (A) Whole-cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by 10% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) Cells were treated with hydrogen peroxide (12.5 μM), and DNA single-strand breaks and alkali-labile sites were measured at various time points postincubation by the alkaline comet assay. Shown are the percentages of tail DNA with standard deviations from the results of at least three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.02; ***, P < 0.01 as analyzed by a one-sample t test of percent tail DNA at the respective time points comparing NT control siRNA- and TRIM26 siRNA- or NTH1 O/E-treated cells. (C) Clonogenic survival of HCT116 cells was analyzed following treatment with increasing doses of hydrogen peroxide (0 to 300 μM). Shown are the mean surviving fractions with standard errors from the results of at least three independent experiments. P < 2.2 × 10−16 (NT siRNA versus TRIM26 siRNA) and P < 2.9 × 10−7 (NT siRNA versus NTH1 O/E) as analyzed by the CFAssay for R package.