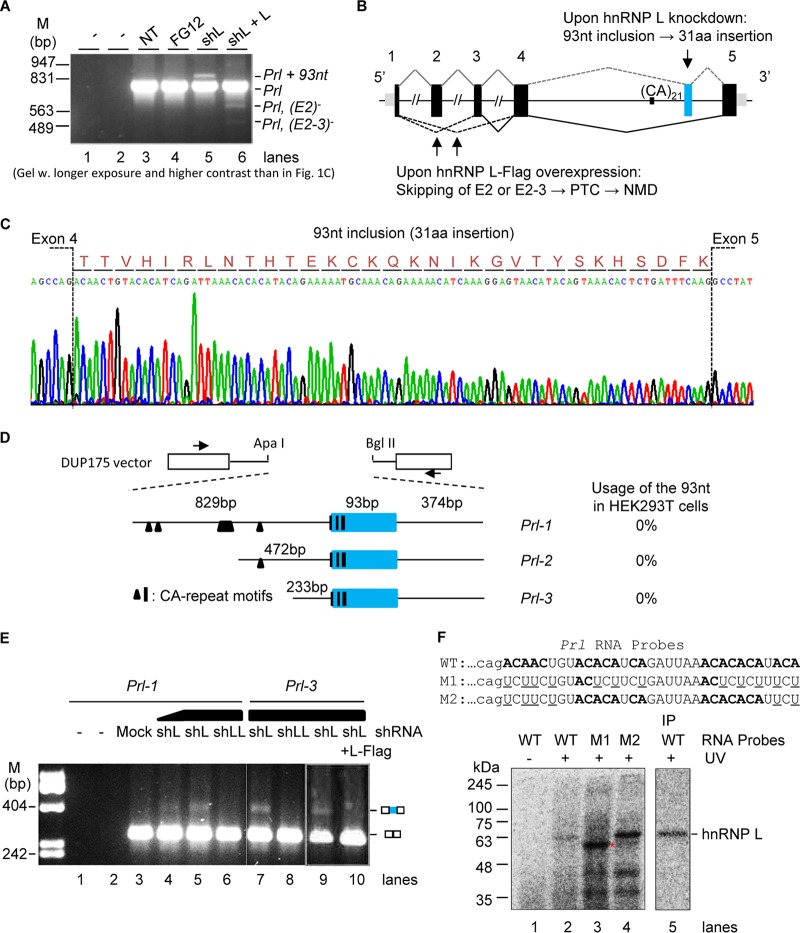
FIG 3.
hnRNP L-specific effect on the usage of a 93-nt cryptic exon of Prl. (A) A high-contrast, long-exposure image of an agarose gel of the RT-PCR products of Prl in GH3 cells. Identities of the different Prl products are to the right of the gel. Note that this gel highlights the longer Prl product and is not quantitative regarding the Prl level compared to that depicted in Fig. 1. (B) Diagram of the Prl variants detected in GH3 cells with different expression levels of hnRNP L. Lines, introns; boxes, exons; narrower boxes, untranslated regions; blue box, the intron piece (cryptic exon) retained in the shL sample. (C) Sequencing chromatogram of the Prl + 93-nt band in the gel shown in panel A. Inclusion of a 93-nt cryptic exon between exons 4 and 5 of Prl caused a 31-aa (amino acid) insertion in the PRL protein. (D) Diagram of the Prl splicing reporter minigenes cloned into the vector DUP175. Black bars and triangles, CA-rich motifs; horizontal lines, introns; blue box, the 93-nt cryptic exon. Test results of the 93-nt usage in the HEK293T cells are on the right. Arrowheads indicate the location of PCR primers. (E) hnRNP L specifically inhibits splicing of the 93-nt cryptic exon. Shown is an agarose gel of the RT-PCR products of Prl minigenes from HEK293T cells with or without hnRNP L or LL knockdown and rescue. Relative amounts of the shRNA viruses used for transduction are 30 μl and 90 μl. Identities of the PCR bands are to the right. (F) UV cross-linking assay of the [α-32P]CTP-labeled Prl RNA probes in HeLa nuclear extracts, followed by immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-hnRNPL. (Top) CA-rich motifs of the Prl RNA probes. (Bottom) Phosphor images of the cross-linked and IP proteins in SDS-PAGE gels. *, uncharacterized protein, likely PTBP1, with increased binding to the mutated sequence motif UCUU, UUCU, or CUCU in M1, as also observed in similar cases by Cao et al. (81). The full 68-nt probe sequence is described in Materials and Methods.