FIG 4.
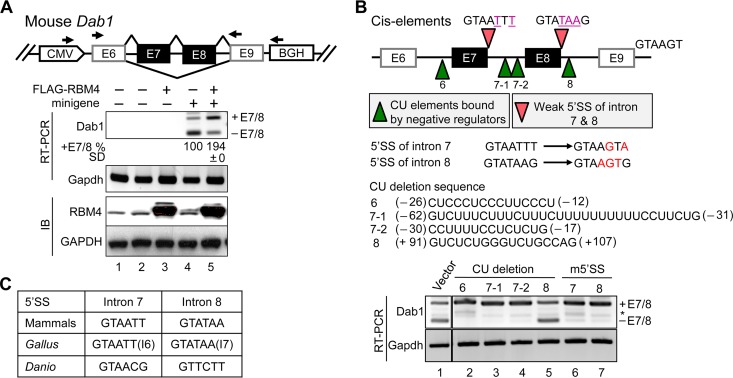
RBM4 regulates alternative exon selection of Dab1. (A) The diagram illustrates the mouse Dab1 minigene and primers used for nested RT-PCR. HEK293 cells were cotransfected with either the empty vector (lanes 1 to 3) or Dab1 minigene (lanes 4 and 5) and either the empty or FLAG-RBM4 expression vector. RT-PCR and immunoblotting were performed to detect the indicated mRNAs (Dab1 and Gapdh) and proteins (RBM4 and GAPDH). Relative exon 7/8 inclusion (i.e., +E7/8 versus total; E12.5 was set as 1) was obtained from three independent experiments. CMV, cytomegalovirus; BGH, bovine growth hormone. (B) The diagram illustrates the mutant Dab1 minigenes that contained a mutated 5′ splice site (m5′SS; pink arrowheads) or lacked each of the indicated CU-rich sequences (green arrowheads); the 5′ SS and CU-rich sequences are indicated below the diagram. The positions of the CU-rich sequences are indicated (−, upstream of exon 6 or 7; +, downstream of exon 8). HEK293 cells were transfected with the wild-type or each of the mutant minigenes; Dab1 minigene splicing products and Gapdh were analyzed by RT-PCR. *, either +E7 or −E7 (C) The 5′ splice site sequences of introns 7/8 of mammalian, Gallus gallus (introns 6/7), and Danio rerio Dab1.