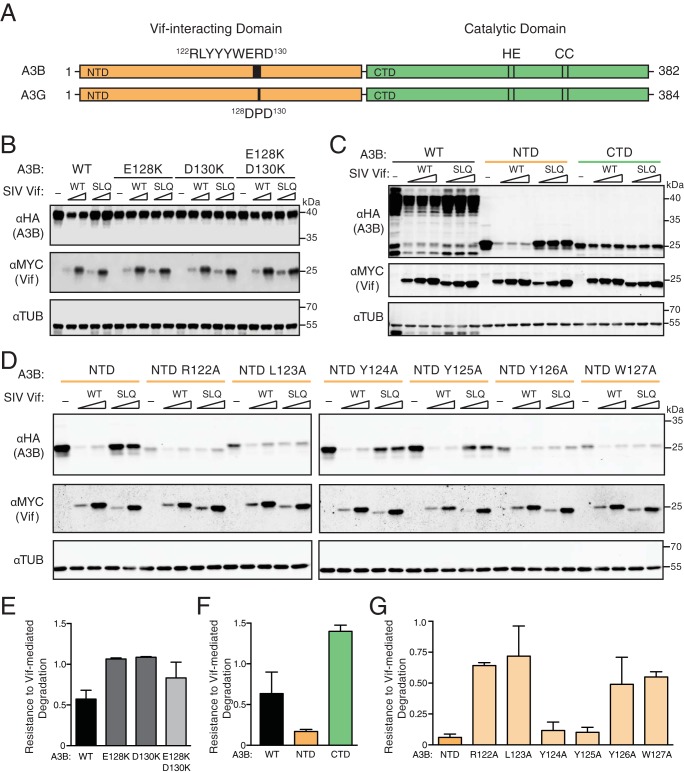
FIG 2.
SIVmac239 Vif interacts with the N-terminal domain of human APOBEC3B. (A) Schematic of human A3B and A3G with N- and C-terminal halves shaded orange and green, respectively. N-terminal Vif-interacting amino acids and C-terminal catalytic domain residues are labeled. (B) Immunoblots of 293T cells expressing full-length human A3B, wild-type (WT) or the indicated mutants, together with SIVmac239 Vif or an SLQ-AAA derivative (SLQ). A3B was detected using an anti-HA antibody for a C-terminal HA epitope tag. Vif was detected using an anti-MYC antibody for a C-terminal MYC epitope tag, and anti-α-tubulin was used as a loading control. (C) Immunoblots of 293T cells expressing full-length human A3B (WT), the N-terminal half (NTD), or the C-terminal half (CTD) together with an empty vector (−), SIVmac239 Vif, or an SLQ-AAA derivative. Analysis was with the same antibodies as for panel B. (D) Immunoblots of 293T cells expressing the N-terminal half of human A3B (NTD) or the indicated single-amino-acid substitution mutants together with an empty vector (−), SIVmac239 Vif, or an SLQ-AAA derivative. Analysis was with the same antibodies as for panel B. (E, F, and G) Quantification of data in panels B, C, and D, respectively. The A3B level of each immunoblot lane was first normalized to tubulin, and then resistance-to-degradation values were calculated as the normalized A3B level in the presence of wild-type SIVmac239 Vif relative to the SIVmac239 Vif SLQ mutant. Each histogram bar reports the mean ± the difference between two independent reactions (E and G) or the mean ± standard deviation from three independent reactions (F).