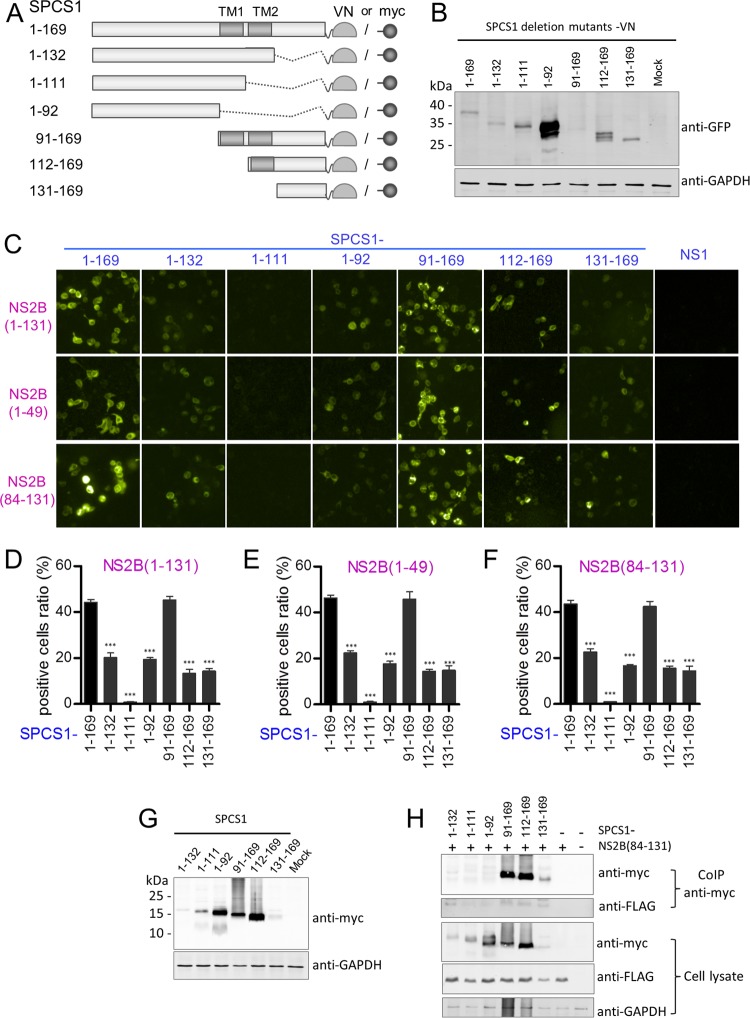
FIG 12.
Interaction of SPCS1 deletion mutants with JEV NS2B, NS2B(1–49), and NS2B(84–131). (A) Schematic diagram of SPCS1 deletion mutant constructs tagged with the N-terminal fragment of the Venus protein or myc. Transmembrane segments are indicated in gray boxes. The locations of SPCS1 deletion mutants are indicated on the left, along with amino acid positions. (B) Expression of VN-tagged SPCS1 deletion mutants. The membrane was probed with mouse monoclonal antibodies against GFP. Data from one experiment of two are shown. (C) Plasmids were cotransfected into HEK-293T cells, images were captured at 12 hpi by using the HCS system, and the ratio of positive cells was determined. Data from one experiment of three are shown. (D) Positive cell ratios for the interaction between SPCS1 deletion mutants and JEV NS2B. (E) Positive cell ratios for the interaction between SPCS1 deletion mutants and JEV NS2B(1–49). (F) Positive cell ratios for the interaction between SPCS1 deletion mutants and JEV NS2B(84–131). The data are pooled from three experiments in duplicate. Statistical significance was determined by analysis of variance with a multiple-comparison correction (***, P < 0.001). (G) Expression of myc-tagged SPCS1 deletion mutants. HEK-293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids, and cell lysates were examined by immunoblotting using anti-myc or anti-GAPDH antibodies. Data from one experiment of two are shown. (H) Cells were cotransfected with JEV NS2B(84–131) and the indicated SPCS1 deletion mutants, and lysates of transfected cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibody. The resulting precipitates and whole-cell lysates used for immunoprecipitation were examined by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG or anti-myc antibodies. Data from one experiment of two are shown.