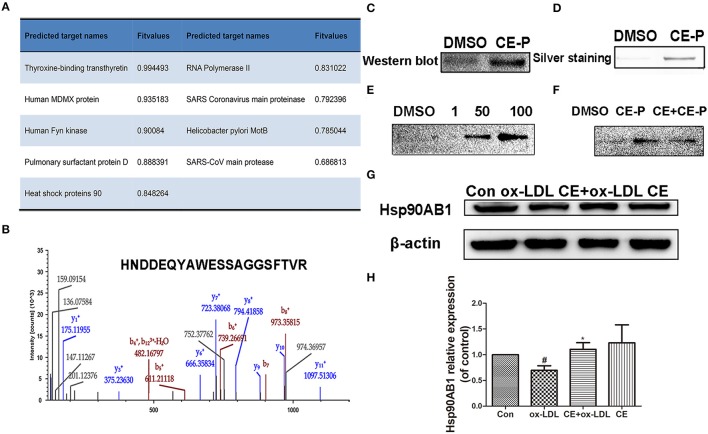
Figure 5.
Hsp90ab1 as potential target of CE-P. (A) The predicted proteins by Discovery Studio 2016 software. (B) Identified peptide of Hsp90ab1 by LC/MS (C) Western-blotting validation of the CE-P target Hsp90ab1 by whole cell lysate pull-down assay. (D) The pull-down assay of the recombinant Hsp90AB1 by CE-P. (E) CE-P could pull down Hsp90AB1 in dose-dependent manner. (F) CE could inhibit the binding to Hsp90AB1 and then the proteins bound to CE-P were detected by Western blot. (G) Effects of CE on Hsp90AB1 expression levels in ox-LDL induced HUVEC damage. Cell lysates were harvested, and Western blot analysis was performed. β-actin expression was examined as the protein loading control. (H) Densitometric analysis was used to quantify the levels of Hsp90AB1. Values are expressed as the mean ± SD #p < 0.05 ox-LDL group vs. control group; *p < 0.05, vs. ox-LDL group.