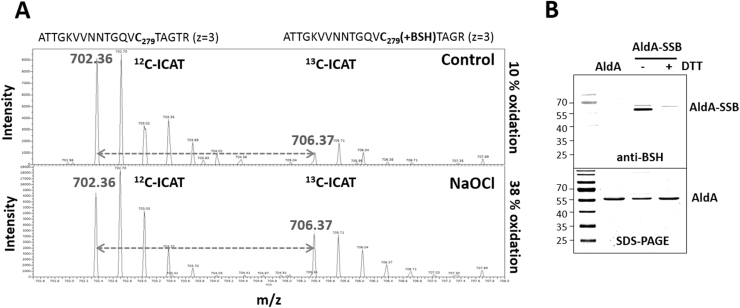
Fig. 1.
OxICAT analysis revealed a 29% increased oxidation of the AldA Cys279-peptide (A) and S-bacillithiolation of the AldA protein in vitro is shown by BSH-specific Western blot analysis (B). (A) The OxICAT mass spectrometry results from the previous study [26] are shown for the AldA-Cys279-peptide in S. aureus under control and 30 min after NaOCl stress. The reduced Cys279-peptides is labelled with light 12C-ICAT, followed by reduction of the S-bacillithiolated Cys279-peptide and labelling with heavy 13C-ICAT reagent. The Cys279-peptide was 10% oxidized in the control and 38% oxidized in the NaOCl stress sample indicating a 29% oxidation increase. (B) AldA is S-bacillithiolated in vitro by H2O2 in the presence of BSH as revealed by BSH-specific Western blots. Reduced purified AldA (40 µM) is pretreated with 10-fold molar excess of BSH (400 µM) and incubated with 10 mM H2O2 for 5 min. The S-bacillithiolated AldA was detected using non-reducing BSH-specific Western blot analysis. The loading control of AldA and S-bacillithiolated AldA (AldA-SSB) is shown as SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie below the anti-BSH blot.